Blocking the RAAS at different levels: an update on the use of the direct renin inhibitors alone and in combination
- PMID: 20730071
- PMCID: PMC2922316
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s11816
Blocking the RAAS at different levels: an update on the use of the direct renin inhibitors alone and in combination
Abstract
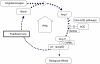
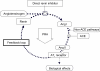
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), an important regulator of blood pressure and mediator of hypertension-related complications, is a prime target for cardiovascular drug therapy. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) were the first drugs to be used to block the RAAS. Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) have also been shown to be equally effective for treatment. Although these drugs are highly effective and are widely used in the management of hypertension, current treatment regimens with ACEIs and ARBs are unable to completely suppress the RAAS. Combinations of ACEIs and ARBs have been shown to be superior than to either agent alone for some, but certainly not all, composite cardiovascular and kidney outcomes, but dual RAAS blockade with the combination of an ACEI and an ARB is sometimes associated with an increase in the risk for adverse events, primarily hyperkalemia and worsening renal function. The recent introduction of the direct renin inhibitor, aliskiren, has made available new combination strategies to obtain a more complete blockade of the RAAS with fewer adverse events. Renin system blockade with aliskiren and another RAAS agent has been, and still is, the subject of many large-scale clinical trials and furthermore, is already available in some countries as a fixed combination.
Keywords: angiotensin II receptor blockers; angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; hypertension; renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system.
Figures
References
-
- Russo D, Minutolo R, Pisani A, et al. Coadministration of losartan and enalapril exerts additive antiproteinuric effect in IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;38(1):18–25. - PubMed
-
- Nakao N, Yoshimura A, Morita H, Takada M, Kayano T, Ideura T. Combination treatment of angiotensin-II receptor blocker and angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor in non-diabetic renal disease (COOPERATE): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361(9352):117–124. - PubMed
-
- Epstein M. Aldosterone as a mediator of progressive renal disease: pathogenetic and clinical implications. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;37(4):677–688. - PubMed
-
- Müller D, Luft F. Direct renin inhibition with aliskiren in hypertension and target organ damage. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1(2):221–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

