The use of social services by community-dwelling older persons who are at risk of institutionalization: a survey
- PMID: 20730084
- PMCID: PMC2921061
- DOI: 10.1007/s10433-010-0150-8
The use of social services by community-dwelling older persons who are at risk of institutionalization: a survey
Abstract
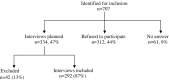
The use of community-based social services additionally to regular home help services to support older persons at risk of institutionalization was studied. Structured interviews were held with 292 persons, who specifically pointed out that they prefer to remain independently at home. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression models were developed to study the association between social service use and personal, health-related and wellbeing characteristics. 195 respondents indicated that they made use of at least one social service (68%). Only three services (individual care, social-cultural activities and restaurant facilities), out of nine, were used regularly. Those who lived in a sheltered environment or were supported by informal caregivers or who visited day care had a significantly higher probability of using these services. More attention should be given to the nature and accessibility of community-based social services in order to have distinctive added value in enabling older persons to age in place.
References
-
- Central Committee on Research Involving Human Subjects (known by the Dutch initials CCMO). Retrieved from www.ccmo.nl
-
- Cox CB. Community care for an aging society. Issues, policies and services. New York: Springer Publishing Company, Inc.; 2005.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources