Characterisation of peptide microarrays for studying antibody-antigen binding using surface plasmon resonance imagery
- PMID: 20730101
- PMCID: PMC2921342
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012152
Characterisation of peptide microarrays for studying antibody-antigen binding using surface plasmon resonance imagery
Abstract
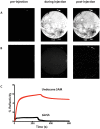
Background: Non-specific binding to biosensor surfaces is a major obstacle to quantitative analysis of selective retention of analytes at immobilized target molecules. Although a range of chemical antifouling monolayers has been developed to address this problem, many macromolecular interactions still remain refractory to analysis due to the prevalent high degree of non-specific binding. We describe how we use the dynamic process of the formation of self assembling monolayers and optimise physical and chemical properties thus reducing considerably non-specific binding and allowing analysis of specific binding of analytes to immobilized target molecules.
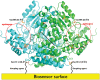
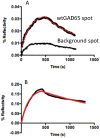
Methodology/principal findings: We illustrate this approach by the production of specific protein arrays for the analysis of interactions between the 65kDa isoform of human glutamate decarboxylase (GAD65) and a human monoclonal antibody. Our data illustrate that we have effectively eliminated non-specific interactions with the surface containing the immobilised GAD65 molecules. The findings have several implications. First, this approach obviates the dubious process of background subtraction and gives access to more accurate kinetic and equilibrium values that are no longer contaminated by multiphase non-specific binding. Second, an enhanced signal to noise ratio increases not only the sensitivity but also confidence in the use of SPR to generate kinetic constants that may then be inserted into van't Hoff type analyses to provide comparative DeltaG, DeltaS and DeltaH values, making this an efficient, rapid and competitive alternative to ITC measurements used in drug and macromolecular-interaction mechanistic studies. Third, the accuracy of the measurements allows the application of more intricate interaction models than simple Langmuir monophasic binding.
Conclusions: The detection and measurement of antibody binding by the type 1 diabetes autoantigen GAD65 represents an example of an antibody-antigen interaction where good structural, mechanistic and immunological data are available. Using SPRi we were able to characterise the kinetics of the interaction in greater detail than ELISA/RIA methods. Furthermore, our data indicate that SPRi is well suited to a multiplexed immunoassay using GAD65 proteins, and may be applicable to other biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cherif B, Roget A, Villiers CL, Calemczuk R, Leroy V, et al. Clinically related protein-peptide interactions monitored in real time on novel peptide chips by surface plasmon resonance imaging. Clin Chem. 2006;52:255–262. - PubMed
-
- Baekkeskov S, Aanstoot HJ, Christgau S, Reetz A, Solimena M, et al. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990;347:151–156. - PubMed
-
- Tuomilehto J, Zimmet P, Mackay IR, Koskela P, Vidgren G, et al. Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase as predictors of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus before clinical onset of disease. Lancet. 1994;343:1383–1385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

