The role of deubiquitinating enzymes in apoptosis
- PMID: 20730552
- PMCID: PMC11115095
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0504-6
The role of deubiquitinating enzymes in apoptosis
Abstract
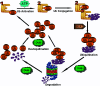
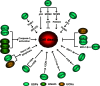
It has become apparent that ubiquitination plays a critical role in cell survival and cell death. In addition, deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) have been determined to be highly important regulators of these processes. Cells can be subjected to various stresses and respond in a variety of different ways ranging from activation of survival pathways to the promotion of cell death, which eventually eliminates damaged cells. The regulatory mechanisms of apoptosis depend on the balanced action between ubiquitination and deubiquitination systems. There is a growing recognition that DUBs play essential roles in regulating several binding partners to modulate the process of apoptosis. Thus, the interplay between the timing of DUB activity and the specificity of ubiquitin attachment and removal from its substrates during apoptosis is important to ensure cellular homeostasis. This review discusses the role of a few ubiquitin-specific DUBs that are involved in either promoting or suppressing the process of apoptosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ube2w and ataxin-3 coordinately regulate the ubiquitin ligase CHIP.Mol Cell. 2011 Aug 19;43(4):599-612. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.05.036. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21855799 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitination regulates the neuroprotective function of the deubiquitinase ataxin-3 in vivo.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 29;288(48):34460-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.513903. Epub 2013 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24106274 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitination directly enhances activity of the deubiquitinating enzyme ataxin-3.EMBO J. 2009 Feb 18;28(4):372-82. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.289. Epub 2009 Jan 15. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19153604 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and cellular roles of ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinating enzymes.Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:363-97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.78.082307.091526. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19489724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein partners of deubiquitinating enzymes.Biochem J. 2008 Sep 1;414(2):161-75. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080798. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18687060 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquitin specific peptidases and prostate cancer.PeerJ. 2023 Feb 16;11:e14799. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14799. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36811009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deubiquitinating Enzyme-Mediated Signaling Networks in Cancer Stem Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 4;12(11):3253. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113253. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33158118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging roles of E3 ubiquitin ligases in ovarian cancer chemoresistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2021 Jun 19;4(2):365-381. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2020.115. eCollection 2021. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 35582023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type 2 deiodinase at the crossroads of thyroid hormone action.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Oct;43(10):1432-41. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.05.016. Epub 2011 Jun 12. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21679772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mcl-1 ubiquitination: unique regulation of an essential survival protein.Cells. 2014 May 8;3(2):418-37. doi: 10.3390/cells3020418. Cells. 2014. PMID: 24814761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glickman MH, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin–proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:373–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

