Enhanced gene and siRNA delivery by polycation-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with chloroquine
- PMID: 20730557
- PMCID: PMC4108588
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-010-0245-0
Enhanced gene and siRNA delivery by polycation-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with chloroquine
Abstract
Purpose: To prepare mesoporous silica-based delivery systems capable of simultaneous delivery of drugs and nucleic acids.
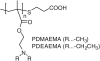
Methods: The surface of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) was modified with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethylmethacrylate) (PDMAEMA) or poly(2-(diethylamino)ethylmethacrylate) (PDEAEMA). The particles were then loaded with a lysosomotropic agent chloroquine (CQ) and complexed with plasmid DNA or siRNA. The ability of the synthesized particles to deliver combinations of CQ and nucleic acids was evaluated using luciferase plasmid DNA and siRNA targeting luciferase and GAPDH.
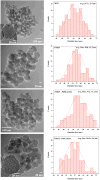
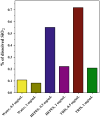
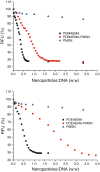
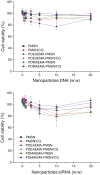
Results: The results show a slow partial MSN dissolution to form hollow silica nanoparticles in aqueous solution. The biological studies show that polycation-modified MSN are able to simultaneously deliver CQ with DNA and siRNA. The co-delivery of CQ and the nucleic acids leads to a significantly increased transfection and silencing activity of the complexes compared with MSN not loaded with CQ.
Conclusion: PEGylated MSN modified with polycations are promising delivery vectors for combination drug/nucleic acid therapies.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018 Mar;8(2):165-177. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018. PMID: 29719777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced gene delivery by polyethyleneimine coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles.Pharm Dev Technol. 2019 Jan;24(1):127-132. doi: 10.1080/10837450.2018.1431930. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Pharm Dev Technol. 2019. PMID: 29357725
-
UV-light cross-linked and pH de-cross-linked coumarin-decorated cationic copolymer grafted mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene co-delivery in vitro.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 Mar;108:110469. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110469. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 31923958
-
Sustained delivery of siRNA/mesoporous silica nanoparticle complexes from nanofiber scaffolds for long-term gene silencing.Acta Biomater. 2018 Aug;76:164-177. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.05.054. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29890267
-
Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Carrier Platform for Intracellular Delivery of Nucleic Acids.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2017 Jun;82(6):655-662. doi: 10.1134/S0006297917060025. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2017. PMID: 28601075 Review.
Cited by
-
Smart polymeric nanoparticles for cancer gene delivery.Mol Pharm. 2015 Feb 2;12(2):314-21. doi: 10.1021/mp500656v. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Mol Pharm. 2015. PMID: 25531409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted siRNA Delivery and mRNA Knockdown Mediated by Bispecific Digoxigenin-binding Antibodies.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2012 Sep 18;1(9):e46. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2012.39. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2012. PMID: 23344238 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in nonviral vectors for gene delivery.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Jul 17;45(7):971-9. doi: 10.1021/ar200151m. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 21870813 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticles for siRNA-Based Gene Silencing in Tumor Therapy.IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2016 Dec;15(8):849-863. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2016.2621730. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2016. PMID: 28092499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-condensation synthesis of well-defined mesoporous silica nanoparticles: effect of surface chemical modification on plasmid DNA condensation and transfection.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017 Dec;11(8):995-1004. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0078. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017. PMID: 29155400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jia J, Zhu F, Ma X, Cao ZW, Li YX, Chen YZ. Mechanisms of drug combinations: interaction and network perspectives. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:111–28. - PubMed
-
- Yadav S, van Vlerken LE, Little SR, Amiji MM. Evaluations of combination MDR-1 gene silencing and paclitaxel administration in biodegradable polymeric nanoparticle formulations to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009;63:711–22. - PubMed
-
- Quist SR, Wang-Gohrke S, Kohler T, Kreienberg R, Runnebaum IB. Cooperative effect of adenoviral p53 gene therapy and standard chemotherapy in ovarian cancer cells independent of the endogenous p53 status. Cancer Gene Ther. 2004;11:547–54. - PubMed
-
- Viitala R, Jokinen M, Tuusa S, Rosenholm JB, Jalonen H. Adjustably bioresorbable sol-gel derived SiO2 matrices for release of large biologically active molecules. J Sol Gel Sci Technol. 2005;36:147–56.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

