Adjuvant activity of GP96 C-terminal domain towards Her2/neu DNA vaccine is fusion direction-dependent
- PMID: 20730610
- PMCID: PMC3024088
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-010-0219-5
Adjuvant activity of GP96 C-terminal domain towards Her2/neu DNA vaccine is fusion direction-dependent
Abstract
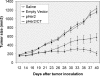
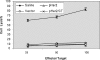
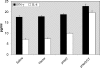
The Her2 is one of tumor-associated antigens (TAA), regarded as an ideal target of immunotherapy. DNA encoding full-length or truncated rat Her2/neu have shown protective and therapeutics potentials against Her2/neu-expressing mammary tumors. However, the efficacy of active vaccination is limited since Her2 is a self-tolerated antigen. Hence, new strategies are required to enhance both the quality and quantity of the immune response against Her2-expressing tumors. Many studies have used Her2/neu gene with cytokine or other molecules involved in regulation of immune response to enhance the potency of Her2/neu DNA vaccines. Some studies fused adjuvant gene to C-terminal domain of Her2/neu gene, while others fused the adjuvant gene N-terminally to Her2/neu gene, but no comparison on how direction of fusion could affect efficiency of DNA vaccine has ever been made. Based on previous reports demonstrating potent adjuvant activity of gp96 C-terminal domain, we chose it as adjuvant. The aim of this study was to investigate if direction of fusion could affect adjuvant activity of gp96 C-terminal domain or potency of Her2/neu DNA vaccination. To do so, we fused C-terminal domain of gp96 to downstream or C-terminal end of transmembrane and extracellular domain (TM+ECD) of rat Her2/neu and resultant immune response to DNA vaccination was evaluated. The results were compared with that of N-terminally fusion of gp96 C-terminal domain to TM+ECD of rat Her2/neu. Our results revealed that adjuvant activity of gp96 C-terminal domain is enhanced when fused N-terminally to TM+ECD of rat Her2/neu. It suggests that adjuvant activity of gp96 C-terminal domain towards Her2/neu is fusion direction-dependent.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of adjuvant activity of N- and C-terminal domain of gp96 in a Her2-positive breast cancer model.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011 Jul;16(4):449-57. doi: 10.1007/s12192-011-0258-6. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011. PMID: 21359667 Free PMC article.
-
N-terminally fusion of Her2/neu to HSP70 decreases efficiency of Her2/neu DNA vaccine.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2010 Sep;15(5):631-8. doi: 10.1007/s12192-010-0175-0. Epub 2010 Mar 12. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2010. PMID: 20224916 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of the non-mutated tumor antigen HER2/neu to mature dendritic cells induces an integrated immune response that protects against breast cancer in mice.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 7;14(2):R39. doi: 10.1186/bcr3135. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22397502 Free PMC article.
-
DNA vaccines expressing antigens with a stress protein-capturing domain display enhanced immunogenicity.Immunol Rev. 2004 Jun;199:54-67. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00136.x. Immunol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15233726 Review.
-
DNA fusion gene vaccines against cancer: from the laboratory to the clinic.Immunol Rev. 2004 Jun;199:156-80. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00145.x. Immunol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15233733 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Mutations in the Fusion Peptide Region of La Crosse Virus Attenuate Neuroinvasion and Confer Protection against Encephalitis.Viruses. 2022 Jul 2;14(7):1464. doi: 10.3390/v14071464. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35891445 Free PMC article.
-
Mini-chaperones: potential immuno-stimulators in vaccine design.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013 Jan;9(1):153-61. doi: 10.4161/hv.22248. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23108356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced specific immune responses by CpG DNA in mice immunized with recombinant hepatitis B surface antigen and HB vaccine.Virol J. 2011 Feb 23;8:78. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-78. Virol J. 2011. PMID: 21342531 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization with recombinant HPV16-E7d in fusion with Flagellin as a cancer vaccine: Effect of antigen-adjuvant orientation on the immune response pattern.Immunol Res. 2025 Feb 13;73(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s12026-025-09598-6. Immunol Res. 2025. PMID: 39939497
-
The critical roles of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones and unfolded protein response in tumorigenesis and anticancer therapies.Oncogene. 2013 Feb 14;32(7):805-18. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.130. Epub 2012 Apr 16. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22508478 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chaput N, Darrasse-Jèze G, Bergot AS, Cordier C, Ngo-Abdalla S, Klatzmann D, et al. Regulatory T cells prevent CD8+ T cell maturation by inhibiting CD4+ Th cells at tumor sites. J Immunol. 2007;179:4969–4978. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

