Methamphetamine induces striatal neurokinin-1 receptor endocytosis primarily in somatostatin/NPY/NOS interneurons and the role of dopamine receptors in mice
- PMID: 20730802
- PMCID: PMC2998568
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.20848
Methamphetamine induces striatal neurokinin-1 receptor endocytosis primarily in somatostatin/NPY/NOS interneurons and the role of dopamine receptors in mice
Abstract
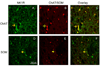
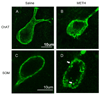
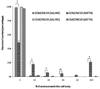
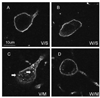
Methamphetamine (METH) is a psychostimulant that induces long-term deficits of dopamine terminal markers and apoptotic cell death in the striatum. Our laboratory demonstrated that pharmacological blockade of the neurokinin-1 receptor attenuated the METH-induced damage to the striatal dopamine terminals and the apoptotic cell death of some striatal neurons. Here, we used histological methods to assess the effect of METH on neurokinin-1 receptor trafficking in the striatum as an indirect index of signaling by the neuropeptide substance P (natural ligand for this receptor). Male mice received a single injection of METH (30 mg/kg, i.p.) and were sacrificed 30 min later. Immunohistofluorescence confocal microscopy confirmed that the neurokinin-1 receptor is located on cholinergic and somatostatin interneurons of the striatum. METH induced the trafficking of the neurokinin-1 receptor from the membrane into cytoplasmic endosomes primarily in the somatostatin/NPY/NOS interneurons, and this phenomenon was attenuated by antagonists of the dopamine D1 (SCH-23390), D2 (raclopride), or neurokinin-1 (WIN-51,708) receptors. These data demonstrate that METH induces the trafficking of the striatal neurokinin-1 receptors principally in the somatostatin/NPY/NOS interneurons and that this phenomenon is dependent on the activity of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Adams DH, Hanson GR, Keefe KA. Differential effects of cocaine and methamphetamine on neurotensin/neuromedin N and preprotachykinin messenger RNA expression in unique regions of the striatum. Neurosci. 2001;102:843–851. - PubMed
-
- Angulo JA, McEwen BS. Molecular aspects of neuropeptide regulation and function in the corpus striatum and nucleus accumbens. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1994;19:1–28. - PubMed
-
- Barak LS, Warabi K, Feng X, Caron MG, Kwatra MM. Real-time visualization of the cellular redistribution of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 and β-arrestin 2 during homologous desensitization of the substance P receptor. J. Biol Chem. 1999;274:7565–7569. - PubMed
-
- Carey JT, Mandel J. A San Francisco Bay Area “speed” scene. J Health Soc Behav. 1968;9:164–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
