Cocaine- and morphine-induced synaptic plasticity in the nucleus accumbens
- PMID: 20730804
- PMCID: PMC3032030
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.20849
Cocaine- and morphine-induced synaptic plasticity in the nucleus accumbens
Abstract
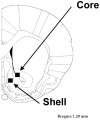
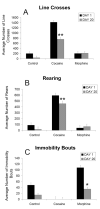
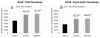
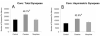
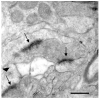
The critical brain areas and molecular mechanisms involved in drug abuse and dependence have been extensively studied. Drug-induced persistent behaviors such as sensitization, tolerance, or relapse, however, far outlast any previously reported mechanisms. A challenge in the field of addiction, therefore, has been to identify drug-induced changes in brain circuitry that may subserve long-lasting changes in behavior. This study examined behavioral changes and electron microscopic evidence of altered synaptic connectivity within the nucleus accumbens (NAc) following repeated administration of cocaine or morphine. The unbiased quantitative stereological physical disector method was used to estimate the number of synapses per neuron. Increases in the synapse-to-neuron ratio were found in the NAc shell of cocaine-treated (49.1%) and morphine-treated (55.1%) rats and in the NAc core of cocaine-treated animals (49.1%). This study provides direct ultrastructural evidence of drug-induced synaptic plasticity and identifies synaptic remodeling as a potential neural substrate underlying drug-induced behavioral sensitization.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Fourth Edition. American Psychiatric Association; Washington DC: 2000. Text Revision.
-
- Anderson BJ, Alcantara AA, Greenough WT. Motor skill learning: changes in synaptic organization of the rat cerebellar cortex. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1996;66:221–229. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SM, Famous KR, Sadri-Vkili G, Kumaresan V, Schmidt HD, Bass CE, Terwilliger EF, Cha JH, Pierce RC. CaMKII: a biochemical bridge linking accumbens dopamine and glutamate systems in cocaine seeking. 2008. - PubMed
-
- Anker RL, Cragg BG. Estimation of the number of synapses in a volume of nervous tissue from counts in thin sections by electron microscopy. J Neurocytol. 1974;3:725–735. - PubMed
-
- Bachtell RK, Choi KH, Simmons DL, Falcon E, Monteggia LM, Neve RL, Self DW. Role of GluR1 expression in nucleus accumbens neurons in cocaine sensitization and cocaine-seeking behavior. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27:2229–22240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
