Effects of moxibustion on dynorphin and endomorphin in rats with chronic visceral hyperalgesia
- PMID: 20731023
- PMCID: PMC2928463
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i32.4079
Effects of moxibustion on dynorphin and endomorphin in rats with chronic visceral hyperalgesia
Abstract
Aim: To observe the analgesic effects of moxibustion in rats with chronic visceral hyperalgesia and its influence on the concentration of dynorphin (Dyn) and endomorphin (EM) in spinal cord.
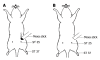
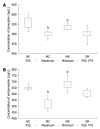
Methods: The rat model of chronic visceral hyperalgesia was established by colorectal distention (CRD). In moxibustion (MX) group, moxibustion was applied once daily for 7 d; in sham moxibustion (SM) group, moxibustion was given to the same acupoints but with the non-smoldered end of the moxa stick. Model control (MC) group and normal control group were also studied. The scoring system of abdominal withdrawal reflex was used to evaluate visceral pain for behavioral assessment. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay was performed to determine the concentrations of Dyn and EM in spinal cord.
Results: Moxibustion significantly decreased visceral pain to CRD in this rat model, and no significant difference was detected between the SM group and the MC group. In MX group, moxibustion also increased the concentrations of Dyn and EM in spinal cord, and no significant difference was found between the SM group and the MC group.
Conclusion: Moxibustion therapy can significantly enhance the pain threshold of rats with chronic visceral hyperalgesia, and the effect may be closely related to the increased concentration of Dyn and EM in spinal cord.
Figures
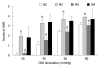
Similar articles
-
Suspended moxibustion relieves chronic visceral hyperalgesia and decreases hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone levels.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Feb 7;17(5):662-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i5.662. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21350717 Free PMC article.
-
Herb-partition moxibustion relieves chronic visceral hyperalgesia and 5-HT concentration in colon mucosa of rats.Neurol Res. 2009 Sep;31(7):734-7. doi: 10.1179/174313209X382313. Epub 2008 Dec 23. Neurol Res. 2009. PMID: 19108755
-
Suspended moxibustion relieves chronic visceral hyperalgesia via serotonin pathway in the colon.Neurosci Lett. 2009 Feb 20;451(2):144-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.12.026. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Neurosci Lett. 2009. PMID: 19114087
-
[Effect of moxibustion of "dachangshu" (BL 25) area on pain reaction and TRPV 1 mRNA expression of bone marrow cells in visceral hyperalgesia rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2013 Feb;38(1):14-9. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2013. PMID: 23650794 Chinese.
-
Moxibustion eases chronic inflammatory visceral pain through regulating MEK, ERK and CREB in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Sep 14;23(34):6220-6230. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6220. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28974888 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Study on the Mechanism Underlying the Regulation of the NMDA Receptor Pathway in Spinal Dorsal Horns of Visceral Hypersensitivity Rats by Moxibustion.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:3174608. doi: 10.1155/2016/3174608. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27200098 Free PMC article.
-
Factorial study of moxibustion in treatment of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 7;20(37):13563-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13563. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25309087 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Suspended moxibustion at Tianshu (ST25) inhibits prokineticin 1 and prokineticin receptor 1 expression in the spinal cord of rats with chronic visceral hypersensitivity.Neural Regen Res. 2012 May 25;7(15):1145-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.15.004. Neural Regen Res. 2012. PMID: 25722707 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying the analgesic effect of moxibustion on visceral pain in irritable bowel syndrome: a review.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:895914. doi: 10.1155/2014/895914. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 25093032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Moxibustion on β-EP and Dyn Levels of Pain-Related Indicators in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Apr 3;2021:6637554. doi: 10.1155/2021/6637554. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33884025 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

