Sequential layer analysis of protein immunosensors based on single wall carbon nanotube forests
- PMID: 20731335
- PMCID: PMC2939275
- DOI: 10.1021/la102306z
Sequential layer analysis of protein immunosensors based on single wall carbon nanotube forests
Abstract
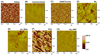
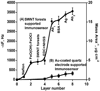
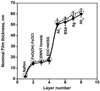
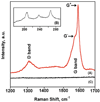
Electrochemical immunosensors using vertically aligned single wall carbon nanotube (SWNT) forests can provide ultrasensitive, accurate cancer biomarker protein assays. Herein we report a systematic investigation of the structure, thickness, and functionality of each layer of these immunosensors using atomic force microscopy (AFM), quartz crystal microbalance (QCM), and scanning white light interferometry (SWLI). This provides a detailed picture of the surface morphology of each layer along with surface concentration and thickness of each protein layer. Results reveal that the major reasons for sensitivity gain can be assigned to the dense packing of carboxylated SWNT forest tips, which translate to a large surface concentration of capture antibodies, together with the high quality of conductive SWNT forests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Designing nanomaterial-enhanced electrochemical immunosensors for cancer biomarker proteins.Bioelectrochemistry. 2009 Sep;76(1-2):189-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2009.03.011. Epub 2009 Apr 5. Bioelectrochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19403342 Free PMC article.
-
Protein immunosensor using single-wall carbon nanotube forests with electrochemical detection of enzyme labels.Mol Biosyst. 2005 May;1(1):70-8. doi: 10.1039/b502124c. Epub 2005 Mar 24. Mol Biosyst. 2005. PMID: 16880966
-
Mediated amperometric immunosensing using single walled carbon nanotube forests.Analyst. 2004 Dec;129(12):1176-80. doi: 10.1039/b412805b. Epub 2004 Nov 12. Analyst. 2004. PMID: 15565214
-
Employing Raman spectroscopy to qualitatively evaluate the purity of carbon single-wall nanotube materials.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2004 Sep;4(7):691-703. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2004.116. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15570946 Review.
-
Development of immunosensors using carbon nanotubes.Biotechnol Prog. 2007 May-Jun;23(3):517-31. doi: 10.1021/bp0602395. Epub 2007 Apr 26. Biotechnol Prog. 2007. PMID: 17458980 Review.
Cited by
-
Voltammetric immunosensor assembled on carbon-pyrenyl nanostructures for clinical diagnosis of type of diabetes.Anal Chem. 2015 Mar 3;87(5):2648-54. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00016. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25675332 Free PMC article.
-
Restricted Proteolysis and LC-MS/MS To Evaluate the Orientation of Surface-Immobilized Antibodies.Anal Chem. 2019 Apr 2;91(7):4913-4919. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01155. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 30840436 Free PMC article.
-
Nanobiosensing with Arrays and Ensembles of Nanoelectrodes.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Dec 30;17(1):65. doi: 10.3390/s17010065. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28042840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inkjet-printed gold nanoparticle electrochemical arrays on plastic. Application to immunodetection of a cancer biomarker protein.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2011 Mar 21;13(11):4888-94. doi: 10.1039/c0cp01755h. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2011. PMID: 21212889 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced nanoengineered-customized point-of-care tools for prostate-specific antigen.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 Dec 14;189(1):27. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-05127-y. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34905090 Review.
References
-
- Bachtold A, Hadley P, Nakanishi T, Dekker C. Science. 2001;294:1317–1320. - PubMed
-
- Lefebvre J, Antonov RD, Radosavljevic M, Lynch JF, Llaguno M, Johnson AT. Carbon. 2000;38:1745–1749.
-
- Bockrath M, Cobden DH, McEuen PL, Chopra NG, Zettl A, Thess A, Smalley RE. Science. 1997;275:1922–1925. - PubMed
-
- Yao Z, Postma HWC, Balents L, Dekker C. Nature. 1999;402:273–276.
-
- Tans SJ, Devoret MH, Dal H, Thess A, Smalley RE, Geerligs LJ, Dekker C. Nature. 1997;386:474–477.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

