Methylene blue reduces aβ levels and rescues early cognitive deficit by increasing proteasome activity
- PMID: 20731659
- PMCID: PMC2992595
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2010.00430.x
Methylene blue reduces aβ levels and rescues early cognitive deficit by increasing proteasome activity
Abstract
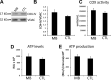
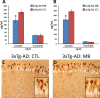
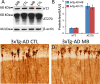
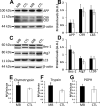
Promising results have emerged from a phase II clinical trial testing methylene blue (MB) as a potential therapeutic for Alzheimer disease (AD), where improvements in cognitive functions of AD patients after 6 months of MB administration have been reported. Despite these reports, no preclinical testing of MB in mammals has been published, and thus its mechanism of action in relation to AD pathology remains unknown. In order to elucidate the effects of MB on AD pathology and to determine its mechanism of action, we used a mouse model (3xTg-AD) that develops age-dependent accumulation of Aβ and tau and cognitive decline. Here, we report that chronic dietary MB treatment reduces Aβ levels and improves learning and memory deficits in the 3xTg-AD mice. The mechanisms underlying the effects of MB on Aβ pathology appears to be mediated by an increase in Aβ clearance as we show that MB increases the chymotrypsin- and trypsin-like activities of the proteasome in the brain. To our knowledge, this is the first report showing that MB increases proteasome function and ameliorates AD-like pathology in vivo. Overall, the data presented here support the use of MB for the treatment of AD and offer a possible mechanism of action.
Figures

References
-
- Atamna H, Nguyen A, Schultz C, Boyle K, Newberry J, Kato H, Ames BN (2008) Methylene blue delays cellular senescence and enhances key mitochondrial biochemical pathways. Faseb J 22:703–712. - PubMed
-
- Billings LM, Oddo S, Green KN, McGaugh JL, LaFerla FM (2005) Intraneuronal Abeta causes the onset of early Alzheimer's disease‐related cognitive deficits in transgenic mice. Neuron 45:675–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

