Roles of light and serotonin in the regulation of gastrin-releasing peptide and arginine vasopressin output in the hamster SCN circadian clock
- PMID: 20731711
- PMCID: PMC2970749
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07374.x
Roles of light and serotonin in the regulation of gastrin-releasing peptide and arginine vasopressin output in the hamster SCN circadian clock
Abstract
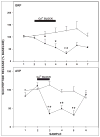
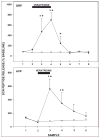
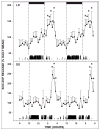
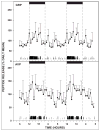
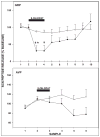
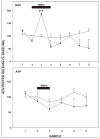
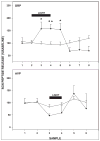
Daily timing of the mammalian circadian clock of the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is regulated by photic input from the retina via the retinohypothalamic tract. This signaling is mediated by glutamate, which activates SCN retinorecipient units communicating to pacemaker cells in part through the release of gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP). Efferent signaling from the SCN involves another SCN-containing peptide, arginine vasopressin (AVP). Little is known regarding the mechanisms regulating these peptides, as literature on in vivo peptide release in the SCN is sparse. Here, microdialysis-radioimmunoassay procedures were used to characterize mechanisms controlling GRP and AVP release in the hamster SCN. In animals housed under a 14/10-h light-dark cycle both peptides exhibited daily fluctuations of release, with levels increasing during the morning to peak around midday. Under constant darkness, this pattern persisted for AVP, but rhythmicity was altered for GRP, characterized by a broad plateau throughout the subjective night and early subjective day. Neuronal release of the peptides was confirmed by their suppression with reverse-microdialysis perfusion of calcium blockers and stimulation with depolarizing agents. Reverse-microdialysis perfusion with the 5-HT(1A,7) agonist 8-OH-DPAT ((±)-8-hydroxydipropylaminotetralin hydrobromide) during the day significantly suppressed GRP but had little effect on AVP. Also, perfusion with the glutamate agonist NMDA, or exposure to light at night, increased GRP but did not affect AVP. These analyses reveal distinct daily rhythms of SCN peptidergic activity, with GRP but not AVP release attenuated by serotonergic activation that inhibits photic phase-resetting, and activated by glutamatergic and photic stimulation that mediate this phase-resetting.
© 2010 The Authors. European Journal of Neuroscience © 2010 Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Abe H, Rusak B, Robertson HA. Photic induction of fos protein in the suprachiasmatic nucleus is inhibited by the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801. Neurosci Lett. 1991;127:9–12. - PubMed
-
- Abe H, Robertson HA, Rusak B. NMDA and non-NMDA receptor antagonists inhibit photic induction of Fos protein in the hamster suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res Bull. 1992;28:831–835. - PubMed
-
- Abrahamson EE, Moore RY. Suprachiasmatic nucleus in the mouse: retinal innervation, intrinsic organization and efferent projections. Brain Res. 2001;916:172–191. - PubMed
-
- Aida R, Moriya T, Araki M, Akiyama M, Wada K, Wada E, Shibata S. Gastrin-releasing peptide mediates photic entrainable signals to dorsal subsets of suprachiasmatic nucleus via induction of Period gene in mice. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;61:26–34. - PubMed
-
- Aioun J, Chambille I, Peytevin J, Martinet L. Neurons containing gastrin-releasing peptide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide are involved in the reception of the photic signal in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the Syrian hamster: an immunocytochemical ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res. 1998;291:239–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

