Sepiapterin reverses the changes in gastric nNOS dimerization and function in diabetic gastroparesis
- PMID: 20731778
- PMCID: PMC3072796
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2010.01588.x
Sepiapterin reverses the changes in gastric nNOS dimerization and function in diabetic gastroparesis
Abstract
Background: We have demonstrated previously that in vivo supplementation of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH₄); a co-factor for neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) significantly restored delayed gastric emptying and attenuated nitrergic relaxation in diabetic rat. In this study, we have investigated whether supplementation of sepiapterin (SEP), a precursor for BH₄ biosynthesis via salvage pathway restores gastric emptying and nitrergic system in female diabetic rats.
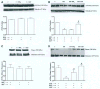
Methods: Diabetic rats (streptozotocin-induced) were supplemented with BH₄ or SEP (20 mg kg⁻¹ body weight). Gastric nitrergic relaxation in the presence or absence of high glucose and SEP were measured by electric field stimulation. Gastric muscular strips from healthy or diabetic female rats were incubated in the presence or absence of high glucose, SEP and/or methotrexate (MTX). Nitric oxide release was measured colorimetrically by NO assay kit. The expression of nNOSα and dimerization was detected by Western blot.
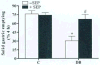
Key results: In vitro studies on gastric muscular tissues showed that MTX, an inhibitor of BH₄ synthesis via salvage pathway, significantly decreased NO release. In vivo treatment with MTX reduced both gastric nitrergic relaxation and nNOSα dimerization. Supplementation of SEP significantly attenuated delayed gastric emptying in diabetic rats. In addition, SEP supplementation restored impaired nitrergic relaxation, gastric nNOSα protein expression, and dimerization in diabetic rats.
Conclusions & inferences: The above data suggests that supplementation of SEP accelerated gastric emptying and attenuated reduced gastric nNOSα expression, and dimerization. Therefore, SEP supplementation is a potential therapeutic option for female patients of diabetic gastroparesis.
© 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impairment of nitrergic system and delayed gastric emptying in low density lipoprotein receptor deficient female mice.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011 Aug;23(8):773-e335. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01695.x. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011. PMID: 21414103 Free PMC article.
-
Sepiapterin alleviates impaired gastric nNOS function in spontaneous diabetic female rodents through NRF2 mRNA turnover and miRNA biogenesis pathway.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Dec 1;315(6):G980-G990. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00152.2018. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30285465 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), a cofactor for nNOS, restores gastric emptying and nNOS expression in female diabetic rats.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010 May;298(5):G692-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00450.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20185690 Free PMC article.
-
Gender bias in gastroparesis: is nitric oxide the answer?Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Sep;56(9):2520-7. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1735-6. Epub 2011 May 11. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21559738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prokinetics in diabetic gastroparesis.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2012 Aug;14(4):297-305. doi: 10.1007/s11894-012-0275-3. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22688694 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of Nrf2 attenuates delayed gastric emptying in obesity induced diabetic (T2DM) female mice.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 May 1;135:132-143. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.02.029. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30831189 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin Va but Not nNOSα is Significantly Reduced in Jejunal Musculomotor Nerve Terminals in Diabetes Mellitus.Front Med (Lausanne). 2014 Jun 20;1:17. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2014.00017. eCollection 2014. Front Med (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 25705628 Free PMC article.
-
S-nitrosothiol signals in the enteric nervous system: lessons learnt from big brother.Front Neurosci. 2011 Mar 9;5:31. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2011.00031. eCollection 2011. Front Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21441985 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of nitrergic system and delayed gastric emptying in low density lipoprotein receptor deficient female mice.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011 Aug;23(8):773-e335. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01695.x. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011. PMID: 21414103 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Diabetes on Salivary Gland Protein Expression of Tetrahydrobiopterin and Nitric Oxide Synthesis and Function.J Periodontol. 2016 Jun;87(6):735-41. doi: 10.1902/jop.2016.150639. Epub 2016 Jan 16. J Periodontol. 2016. PMID: 26777763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vijay SV, Lyford G, Gores G, Farrugia G. Nitric oxide in gastrointestinal health and disease. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:903–13. - PubMed
-
- Toda N, Herman AG. Gastrointestinal function regulation by nitrergic efferent nerves. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57:315–38. - PubMed
-
- Holzer P, Schicho R, Holzer-Petsche U, Lippe IT. The gut as a neurological organ. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2001;113:647–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

