Biological characteristics and treatment outcomes of metastatic or recurrent neuroendocrine tumors: tumor grade and metastatic site are important for treatment strategy
- PMID: 20731845
- PMCID: PMC2936327
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-448
Biological characteristics and treatment outcomes of metastatic or recurrent neuroendocrine tumors: tumor grade and metastatic site are important for treatment strategy
Abstract
Background: Studies about the biology, treatment pattern, and treatment outcome of metastatic/recurrent neuroendocrine tumor (NET) have been few.
Methods: We enrolled patients with metastatic/recurrent NET diagnosed between January 1996 and July 2007 and retrospectively analyzed.
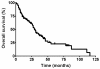
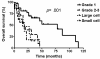
Results: A total of 103 patients were evaluated. Twenty-six patients (25.2%) had pancreatic NET, 27 (26.2%) had gastrointestinal NET, 2 (1.9%) had lung NET, 28 (27.2%) had NET from other sites, and 20 (19.4%) had NET from unknown origin. The liver was the most common metastatic site (68.9%). Thirty-four patients had grade 1 disease, 1 (1.0%) had grade 2 disease, 15 (14.6%) had grade 3 disease, 9 (8.7%) had large cell disease, and 7 (6.8%) had small cell disease.Sixty-six patients received systemic treatment (interferon, somatostatin analogues or chemotherapy), 64 patients received local treatment (TACE, radiofrequency ablation, metastasectomy, etc.). Thirty-six patients received both systemic and local treatments.Median overall survival (OS) was 29.0 months (95% confidence interval, 25.0-33.0) in the 103 patients. OS was significantly influenced by grade (p = .001). OS was 43.0, 23.0, and 29.0 months in patients who received local treatment only, systemic treatment only, and both treatments, respectively (p = .245). The median time-to-progression (TTP) was 6.0 months. Overall response rate was 34.0% and disease-control rate was 64.2%. TTP was influenced by the presence of liver metastasis (p = .011).
Conclusions: OS of metastatic/recurrent NET was different according to tumor grade. TTP was different according to metastasis site. Therefore, development of optimal treatment strategy based on the characteristics of NET is warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical course of neuroendocrine tumors with different origins (the pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, and lung).Am J Clin Oncol. 2012 Dec;35(6):549-56. doi: 10.1097/COC.0b013e31821dee0f. Am J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 21659833
-
Multimodal Therapy of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Anus With Distant Metastasis: A Single-Institution Experience.Dis Colon Rectum. 2017 Aug;60(8):785-791. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000000827. Dis Colon Rectum. 2017. PMID: 28682963
-
Extracerebral metastases determine the outcome of patients with brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2010 Sep 7;10:480. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-480. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20819239 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic surgery for metastases from neuroendocrine tumors.Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2003 Jan;12(1):231-42. doi: 10.1016/s1055-3207(02)00076-5. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2003. PMID: 12735141 Review.
-
Colorectal cancer: Metastases to a single organ.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 7;21(41):11767-76. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11767. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26557001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The expanding role of somatostatin analogs in gastroenteropancreatic and lung neuroendocrine tumors.Drugs. 2015 May;75(8):847-58. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0397-7. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25911185 Review.
-
Long-term management of a patient with well-differentiated pulmonary neuroendocrine carcinoma: a case report.Case Rep Oncol. 2013 Apr 6;6(1):209-15. doi: 10.1159/000350745. Print 2013 Jan. Case Rep Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23626563 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the initial site of metastases on post-recurrence survival for neuroendocrine cervical cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jun 14;22(1):655. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09737-4. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35698184 Free PMC article.
-
Incidental metastatic mediastinal atypical carcinoid in a patient with parathyroid adenoma: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2017 Mar 26;11(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13256-017-1234-2. J Med Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28342443 Free PMC article.
-
Initial clinical evaluation of indigenous 90Y-DOTATATE in sequential duo-PRRT approach (177Lu-DOTATATE and 90Y-DOTATATE) in neuroendocrine tumors with large bulky disease: Observation on tolerability, 90Y-DOTATATE post- PRRT imaging characteristics (bremsstrahlung and PETCT) and early adverse effects.World J Nucl Med. 2020 Oct 2;20(1):73-81. doi: 10.4103/wjnm.WJNM_52_20. eCollection 2021 Jan-Mar. World J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 33850492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ransom WB. A case of primary carcinoma of the ileum. Lancet. 1890;2:1020–1023. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)64173-9. - DOI
-
- Moertel CG, Kvols LK, O'Connell MJ, Rubin J. Treatment of neuroendocrine carcinomas with combined etoposide and cisplatin. Evidence of major therapeutic activity in the anaplastic variants of these neoplasms. Cancer. 1991;68(2):227–232. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910715)68:2<227::AID-CNCR2820680202>3.0.CO;2-I. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yao JC, Hassan M, Phan A, Dagohoy C, Leary C, Mares JE, Abdalla EK, Fleming JB, Vauthey JN, Rashid A. et al.One hundred years after "carcinoid": epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(18):3063–3072. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.4377. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous