Interferon-β attenuates lung inflammation following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage
- PMID: 20731855
- PMCID: PMC2945141
- DOI: 10.1186/cc9232
Interferon-β attenuates lung inflammation following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage
Abstract
Introduction: Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) affects relatively young people and carries a poor prognosis with a case fatality rate of 35%. One of the major systemic complications associated with SAH is acute lung injury (ALI) which occurs in up to one-third of the patients and is associated with poor outcome. ALI in SAH may be predisposed by neurogenic pulmonary edema (NPE) and inflammatory mediators. The objective of this study was to assess the immunomodulatory effects of interferon-β (IFN-β) on inflammatory mediators in the lung after experimental SAH.
Methods: Male Wistar rats were subjected to the induction of SAH by means of the endovascular filament method. Sham-animals underwent sham-surgery. Rats received IFN-β for four consecutive days starting at two hours after SAH induction. After seven days, lungs were analyzed for the expression of inflammatory markers.
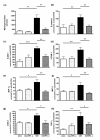
Results: SAH induced the influx of neutrophils into the lung, and enhanced expression of the pulmonary adhesion molecules E-selectin, inter-cellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1, and vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1 compared to sham-animals. In addition, SAH increased the expression of the chemokines macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1α, MIP-2, and cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant (CINC)-1 in the lung. Finally, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) was significantly increased in lungs from SAH-animals compared to sham-animals. IFN-β effectively abolished the SAH-induced expression of all pro-inflammatory mediators in the lung.
Conclusions: IFN-β strongly reduces lung inflammation after experimental SAH and may therefore be an effective drug to prevent SAH-mediated lung injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of S100A9 alleviates neurogenic pulmonary edema after subarachnoid hemorrhage.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Dec;218:115905. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115905. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37949322
-
Dexmedetomidine attenuates subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced acute lung injury through regulating autophagy and TLR/NFκB signaling pathway.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2022 Dec;75(6):518-529. doi: 10.4097/kja.22165. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 35912428 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of ebselen on neutrophil recruitment, chemokine, and inflammatory mediator expression in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation.J Immunol. 2002 Jul 15;169(2):974-82. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.2.974. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12097404
-
The harmful effects of subarachnoid hemorrhage on extracerebral organs.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:858496. doi: 10.1155/2014/858496. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25110700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroinflammatory response after subarachnoid hemorrhage: A review of possible treatment targets.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2025 May;252:108843. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2025.108843. Epub 2025 Mar 16. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2025. PMID: 40107192 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurogenic pulmonary edema caused by spontaneous cerebellar hemorrhage: A fatal case report.Surg Neurol Int. 2014 Jun 30;5:103. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.135579. eCollection 2014. Surg Neurol Int. 2014. PMID: 25101198 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammation after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 30;24(13):10943. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310943. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of α - and β -Adrenergic Mechanisms to the Development of Pulmonary Edema.Scientifica (Cairo). 2012;2012:829504. doi: 10.6064/2012/829504. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012. PMID: 24278744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain-lung interactions and mechanical ventilation in patients with isolated brain injury.Crit Care. 2021 Oct 13;25(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03778-0. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 34645485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythropoietin Inhibits the Increase of Pulmonary Labile Zinc and the Expression of Inflammatory Mediators Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats.Neurocrit Care. 2016 Jun;24(3):472-80. doi: 10.1007/s12028-015-0219-5. Neurocrit Care. 2016. PMID: 26627226
References
-
- Solenski NJ, Haley EC Jr, Kassell NF, Kongable G, Germanson T, Truskowski L, Torner JC. Medical complications of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a report of the multicenter, cooperative aneurysm study. Participants of the Multicenter Cooperative Aneurysm Study. Crit Care Med. 1995;23:1007–1017. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199506000-00004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

