Outcome and prognostic factors of desmoplastic medulloblastoma treated within a multidisciplinary treatment concept
- PMID: 20731859
- PMCID: PMC2939548
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-450
Outcome and prognostic factors of desmoplastic medulloblastoma treated within a multidisciplinary treatment concept
Abstract
Background: Desmoplasia in medulloblastoma is often diagnosed in adult patients and was repeatedly associated with improved results. Today, all medulloblastoma patients receive intensive multimodal treatment including surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy. This study was set up to investigate treatment outcome and prognostic factors after radiation therapy in patients with desmoplastic medulloblastomas.
Methods: Twenty patients treated for desmoplastic medulloblastoma in the Department of Radiation Oncology at the University of Heidelberg between 1984 and 2007 were included. Data were collected retrospectively. Tumor resection was performed in all patients. All patients underwent postsurgical radiotherapy (RT). Two patients underwent whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT), and 18 patients received craniospinal irradiation (CSI). In all patients, an additional boost was delivered to the posterior fossa. The median dose to the whole brain and the craniospinal axis was 35.2 Gray (Gy), and 54.4 Gy to the posterior fossa. Fourteen patients received chemotherapy, including seven who were treated with combined radiochemotherapy and twelve who received adjuvant chemotherapy. Statistical analysis was performed using the log-rank test and the Kaplan-Meier method.
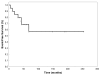
Results: Median follow-up was 59 months. Overall (OS), local (LPFS) and distant progression-free survival (DPFS) was 80%, 71.2%, and 83.3% at 60 months. Patients who suffered from local or distant relapses had significantly worse outcome. Five patients died from recurrent medulloblastoma. Treatment-associated toxicity was acceptable.
Conclusions: Multimodal approaches with surgical resection followed by chemoirradiation achieved high response rates with long OS in desmoplastic medulloblastoma patients. Staging parameters expected to predict for poor prognosis did not significantly influence outcome. However, success of any first line regimen had strong impact on disease control, and remission was achieved in no patient with relapsing disease. Multimodal concepts must be evaluated in further clinical trials.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Outcome and prognostic factors of radiation therapy for medulloblastoma.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 Nov 1;81(3):e7-e13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.12.042. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 21345611
-
Treatment results of adults and children with medulloblastoma NCI, Cairo University experience.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2008 Jun;20(2):175-86. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2008. PMID: 20029474
-
Treatment of adult nonmetastatic medulloblastoma patients according to the paediatric HIT 2000 protocol: a prospective observational multicentre study.Eur J Cancer. 2013 Mar;49(4):893-903. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.10.006. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Eur J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23182688
-
Adult medulloblastoma: multiagent chemotherapy.Neuro Oncol. 2001 Jan;3(1):29-34. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/3.1.29. Neuro Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11305414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medulloblastoma in adults: clinical characteristics and treatment.Cancer Treat Rev. 1999 Feb;25(1):3-12. doi: 10.1053/ctrv.1998.0096. Cancer Treat Rev. 1999. PMID: 10212586 Review.
Cited by
-
Patterns of Failure Following Multimodal Treatment for Medulloblastoma: Long-Term Follow-up Results at a Single Institution.Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Oct;47(4):879-88. doi: 10.4143/crt.2014.067. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 25648090 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of treatment and clinical characteristics on the survival of children with medulloblastoma in Mexico.Front Oncol. 2024 May 2;14:1376574. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1376574. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38756654 Free PMC article.
-
Craniospinal Irradiation in Medulloblastoma using High Energy Medical Linear Accelerator: an Innovative Approach to Planning Technique.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2019 Apr 1;9(2):151-160. eCollection 2019 Apr. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2019. PMID: 31214520 Free PMC article.
-
The Satisfactory Surgical Outcome of Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors in Children at Civil Hospital, Karachi.Asian J Neurosurg. 2020 May 29;15(2):377-381. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_56_19. eCollection 2020 Apr-Jun. Asian J Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32656135 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric medulloblastoma - update on molecular classification driving targeted therapies.Front Oncol. 2014 Jul 22;4:176. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00176. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25101241 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Russel DSRL. Pathology of tumors of the central nervous system. 5 1989.
-
- Carrie C, Lasset C, Alapetite C, Haie-Meder C, Hoffstetter S, Demaille MC, Kerr C, Wagner JP, Lagrange JL, Maire JP. et al.Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in adult patients with medulloblastoma. Retrospective study of 156 patients. Cancer. 1994;74(8):2352–2360. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19941015)74:8<2352::AID-CNCR2820740821>3.0.CO;2-H. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Haie-Meder C, Song PY. Medulloblastoma: differences in adults and children--regarding Frost et al., IJROBP 32:951-957; 1995 and Prados et al., IJROBP 32:1145-1152; 1995. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;32(4):1255–1257. - PubMed
-
- Ertas G, Ucer AR, Altundag MB, Durmus S, Calikoglu T, Ozbagi K, Abanuz H, Altundag K, Demirkasimoglu A. Medulloblastoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor in adults: prognostic factors and treatment results: a single-center experience from Turkey. Med Oncol. 2008;25(1):69–72. doi: 10.1007/s12032-007-0044-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

