Increases in B-type natriuretic peptide after acute mental stress in heart failure patients are associated with alcohol consumption
- PMID: 20731986
- PMCID: PMC2930511
- DOI: 10.15288/jsad.2010.71.786
Increases in B-type natriuretic peptide after acute mental stress in heart failure patients are associated with alcohol consumption
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate in heart failure (HF) patients whether acute mental stress induces increases in the HF-severity biomarker B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and if alcohol consumption is associated with such stress-induced increases.
Method: Twenty-one male HF patients and 19 male non-HF controls (M = 56 years, SEM = 2) underwent a 15-minute acute mental stress test combining public speaking and mental arithmetic. Plasma levels of BNP were determined immediately before as well as 2 hours after the stress test. Alcohol consumption was assessed by self-reported number of drinks per month and history of use.
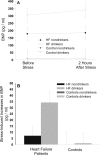
Results: HF patients had higher BNP levels before and after stress, F(1, 38) = 23.42, p < .001, and showed greater stress-induced increases in BNP levels, F(1, 38) = 4.52, p = .04, compared with controls. HF status (beta = .32, p = .015, deltaR(2) = .10) and higher alcohol consumption ((beta = .61, p< .001, deltaR(2) = .37) were independently associated with higher BNP stress increases. Moreover, higher alcohol consumption moderated the greater BNP stress increases in HF patients but not in controls (p = .49, p < .001, delta(2) = .20), although alcohol consumption did not differ between groups.
Conclusions: For individuals with HF, particularly those who drink moderate to more substantial amounts of alcohol, exposure to acute psychological stress leads to increases in circulating levels of BNP, a biomarker which is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in HF.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Molar Ratio of N-terminal pro-B-type Natriuretic Peptide/B-type Natriuretic Peptide for Heart Failure-related Events in Stable Outpatients with Cardiovascular Risk Factors.Intern Med. 2018 Sep 15;57(18):2621-2630. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0471-17. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29709934 Free PMC article.
-
Brain natriuretic peptide and n-terminal brain natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of heart failure in patients with acute shortness of breath.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003 Aug 20;42(4):728-35. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00787-3. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. PMID: 12932611
-
Comparable increase of B-type natriuretic peptide and amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels in patients with severe sepsis, septic shock, and acute heart failure.Crit Care Med. 2006 Aug;34(8):2140-4. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000229144.97624.90. Crit Care Med. 2006. PMID: 16763507
-
Changes of natriuretic peptides predict hospital admissions in patients with chronic heart failure: a meta-analysis.JACC Heart Fail. 2014 Apr;2(2):148-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2013.11.007. JACC Heart Fail. 2014. PMID: 24720923 Review.
-
B-type natriuretic peptide as a biomarker beyond heart failure: speculations and opportunities.Mayo Clin Proc. 2005 Aug;80(8):1029-36. doi: 10.4065/80.8.1029. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005. PMID: 16092582 Review.
Cited by
-
Corin Missense Variants, Blood Pressure, and Hypertension in 11 322 Black Individuals: Insights From REGARDS and the Jackson Heart Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Jun 21;11(12):e025582. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.025582. Epub 2022 Jun 14. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35699180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alderman MH, Ooi WL, Madhavan S, Cohen H. Blood pressure reactivity predicts myocardial infarction among treated hypertensive patients. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 1990;43:859–866. - PubMed
-
- Babyak MA. What you see may not be what you get: A brief, nontechnical introduction to overfitting in regression-type models. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2004;66:411–421. - PubMed
-
- Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1986;51:1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Beilin LJ, Puddey IB. Alcohol and hypertension: An update. Hypertension. 2006;47:1035–1038. - PubMed
-
- Ciampi Q, Borzillo G, Barbato E, Petruzziello B, Betocchi S, Villari B. Diastolic function and BNP changes during exercise predict oxygen consumption in chronic heart failure patients. Scandinavian Cardiovascular Journal. 2009;43:17–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

