Chapter 3. High-throughput protein purification for x-ray crystallography and NMR
- PMID: 20731990
- PMCID: PMC3366499
- DOI: 10.1016/S0065-3233(07)75003-9
Chapter 3. High-throughput protein purification for x-ray crystallography and NMR
Abstract
In structural biology, the most critical issue is the availability of high-quality samples. "Structural-biology-grade" proteins must be generated in a quantity and quality suitable for structure determination using X-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance. The additional challenge for structural genomics is the need for high numbers of proteins at low cost where protein targets quite often have low sequence similarities, unknown properties and are poorly characterized. The purification procedures must reproducibly yield homogeneous proteins or their derivatives containing marker atom(s) in milligram quantities. The choice of protein purification and handling procedures plays a critical role in obtaining high-quality protein samples. Where the ultimate goal of structural biology is the same-to understand the structural basis of proteins in cellular processes, the structural genomics approach is different in that the functional aspects of individual protein or family are not ignored, however, emphasis here is on the number of unique structures, covering most of the protein folding space and developing new technologies with high efficiency. At the Midwest Center Structural Genomics (MCSG), we have developed semiautomated protocols for high-throughput parallel protein purification. In brief, a protein, expressed as a fusion with a cleavable affinity tag, is purified in two immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) steps: (i) first IMAC coupled with buffer-exchange step, and after tag cleavage using TEV protease, (ii) second IMAC and buffer exchange to clean up cleaved tags and tagged TEV protease. Size exclusion chromatography is also applied as needed. These protocols have been implemented on multidimensional chromatography workstations AKTAexplorer and AKTAxpress (GE Healthcare). All methods and protocols used for purification, some developed in MCSG, others adopted and integrated into the MCSG purification pipeline and more recently the Center for Structural Genomics of Infectious Disease (CSGID) purification pipeline, are discussed in this chapter.
Figures
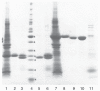
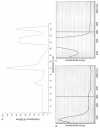

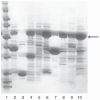
Similar articles
-
High-throughput protein purification and quality assessment for crystallization.Methods. 2011 Sep;55(1):12-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2011.07.010. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Methods. 2011. PMID: 21907284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automation of protein purification for structural genomics.J Struct Funct Genomics. 2004;5(1-2):111-8. doi: 10.1023/B:JSFG.0000029206.07778.fc. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2004. PMID: 15263850 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput protein production and purification at the Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Disease.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011 Sep 1;67(Pt 9):1010-4. doi: 10.1107/S1744309111018367. Epub 2011 Aug 13. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011. PMID: 21904042 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of protein samples for NMR structure, function, and small-molecule screening studies.Methods Enzymol. 2011;493:21-60. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381274-2.00002-9. Methods Enzymol. 2011. PMID: 21371586 Free PMC article.
-
Structural genomics and drug discovery for infectious diseases.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2009 Nov;9(5):507-17. doi: 10.2174/187152609789105713. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19860716 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crystal Structures of the SpoIID Lytic Transglycosylases Essential for Bacterial Sporulation.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jul 15;291(29):14915-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.729749. Epub 2016 May 18. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27226615 Free PMC article.
-
A novel polyamine allosteric site of SpeG from Vibrio cholerae is revealed by its dodecameric structure.J Mol Biol. 2015 Mar 27;427(6 Pt B):1316-1334. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Jan 23. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25623305 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Tandem-Tag Purification Strategy for Challenging Disordered Proteins.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 26;12(11):1566. doi: 10.3390/biom12111566. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358915 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the mechanism of type I dehydroquinate dehydratases from structures of reaction intermediates.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 4;286(5):3531-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.192831. Epub 2010 Nov 18. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21087925 Free PMC article.
-
A fully automated procedure for the parallel, multidimensional purification and nucleotide loading of the human GTPases KRas, Rac1 and RalB.Protein Expr Purif. 2017 Apr;132:75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2017.01.010. Epub 2017 Jan 28. Protein Expr Purif. 2017. PMID: 28137655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Accelerated Technologies Center for Gene to 3D Structure (ATCG3D) http://atcg3d.org/default.aspx.
-
- Berkeley Structural Genomics Center (BSGC) http://www.strgen.org/
-
- Bhikhabhai R, Sjöberg A, Hedkvist L, Galin M, Liljedahl P, Frigård T, Pettersson N, Nilsson M, Sigrell-Simon JA, Markeland-Johansson C. Production of milligram quantities of affinity tagged-proteins using automated multistep chromatographic purification. J Chromatogr A. 2005;1080:83–92. - PubMed
-
- Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics (CESG) http://www.uwstructuralgenomics.org/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

