Environmental enrichment exerts sex-specific effects on emotionality in C57BL/6J mice
- PMID: 20732356
- PMCID: PMC3727905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.08.019
Environmental enrichment exerts sex-specific effects on emotionality in C57BL/6J mice
Abstract
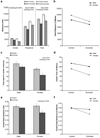
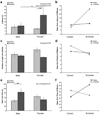
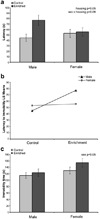
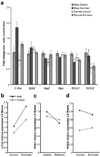
Environmental enrichment (EE) has been shown to exert various behavioral and mood effects in rodents including emotionality, which has a high propensity to be influenced by sex. However, there are only a few comparative studies evaluating the effect of EE and their results are both inconsistent and inconclusive. In the present study, male and female C57BL/6J adolescent mice were housed in either physical enrichment or standard conditions for four weeks with analysis of affective behaviors in the open field, elevated T-maze and forced swim tests. Hippocampal gene expression was characterized in an additional group of mice. In the open field test, exploration was similarly inhibited by EE in male and female mice. Both sex and housing condition influenced the time mice spent in the center of the arena. In the elevated T-maze, anxiety-like behavior was increased in female and decreased in male mice following EE. We observed a trend for EE-induced inhibition of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) mRNA expression in male but not in female mice. In contrast, mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) expression was unaffected by 10 days of physical enrichment but was lower in female mice compared to male mice. Our data suggest that the balance between hippocampal GR and MR may contribute to the observed sex-specific effect of physical enrichment on emotionality-related behavior.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exposure to enriched environment restores the mRNA expression of mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors in the hippocampus and ameliorates depressive-like symptoms in chronically stressed rats.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2011 Nov;8(4):286-93. doi: 10.2174/156720211798121025. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 22023615
-
Adaptation to single housing is dynamic: Changes in hormone levels, gene expression, signaling in the brain, and anxiety-like behavior in adult male C57Bl/6J mice.Horm Behav. 2019 Aug;114:104541. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2019.06.005. Epub 2019 Jul 20. Horm Behav. 2019. PMID: 31220462 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of short-term and long-term environmental enrichment on locomotion, mood-like behavior, cognition and hippocampal gene expression.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Aug 5;368:111917. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.111917. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31004685
-
Neurobiological correlates of individual differences in novelty-seeking behavior in the rat: differential expression of stress-related molecules.J Neurosci. 2000 Sep 15;20(18):6983-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-18-06983.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10995843 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal stress programs neuroendocrine stress responses and affective behaviors in second generation rats in a sex-dependent manner.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015 Dec;62:204-16. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.08.010. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015. PMID: 26318631 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The clinical implications of mouse models of enhanced anxiety.Future Neurol. 2011 Jul 1;6(4):531-571. doi: 10.2217/fnl.11.34. Future Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21901080 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience priming: Translational models for understanding resiliency and adaptation to early life adversity.Dev Psychobiol. 2019 Apr;61(3):350-375. doi: 10.1002/dev.21775. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Dev Psychobiol. 2019. PMID: 30311210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental Enrichment Components Required to Reduce Methamphetamine-Induced Behavioral Sensitization in Mice: Examination of Behaviors and Neural Substrates.J Clin Med. 2022 May 28;11(11):3051. doi: 10.3390/jcm11113051. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35683439 Free PMC article.
-
Mice in Bion-M 1 space mission: training and selection.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 18;9(8):e104830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104830. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25133741 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive response to a future life challenge: consequences of early-life environmental complexity in dual-purpose chicks.J Anim Sci. 2020 Nov 1;98(11):skaa348. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa348. J Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 33111138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramov U, Puussaar T, Raud S, Kurrikoff K, Vasar E. Behavioural differences between C57BL/6 and 129S6/SvEv strains are reinforced by environmental enrichment. Neurosci Lett. 2008;443:223–227. - PubMed
-
- Adamec R, Head D, Blundell J, Burton P, Berton O. Lasting anxiogenic effects of feline predator stress in mice: sex differences in vulnerability to stress and predicting severity of anxiogenic response from the stress experience. Physiol Behav. 2006;88:12–29. - PubMed
-
- Belanoff JK, Rothschild AJ, Cassidy F, DeBattista C, Baulieu EE, Schold C, et al. An open label trial of C-1073 (mifepristone)for psychotic major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2002;52:386–392. - PubMed
-
- Belz EE, Kennell JS, Czambel RK, Rubin RT, Rhodes ME. Environmental enrichment lowers stress-responsive hormones in singly housed male and female rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003;76:481–486. - PubMed
-
- Belzung C, Griebel G. Measuring normal and pathological anxiety-like behaviour in mice: a review. Behav Brain Res. 2001;125:141–149. - PubMed

