Integrating epidermal growth factor receptor assay with clinical parameters improves risk classification for relapse and survival in head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 20732768
- PMCID: PMC2992592
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.05.024
Integrating epidermal growth factor receptor assay with clinical parameters improves risk classification for relapse and survival in head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) overexpression has been consistently found to be an independent predictor of local-regional relapse (LRR) after radiotherapy. We assessed the extent by which it can refine risk classification for overall survival (OS) and LRR in patients with head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).
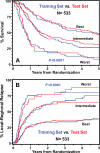
Methods and materials: EGFR expression in locally advanced HNSCC was measured by immunohistochemistry in a series of patients randomized to receive accelerated or conventional radiation regimens in a Phase III trial. Subsequently, data of the two series were pooled (N = 533) for conducting a recursive partitioning analysis that incorporated clinical parameters (e.g., performance status, primary site, T and N categories) and four molecular markers (EGFR, p53, Ki-67, and microvessel density).
Results: This study confirmed that patients with higher than median levels of tumor EGFR expression had a lower OS (relative risk [RR]: 1.90, p = 0.0010) and a higher LRR (RR: 1.91, p = 0.0163). Of the four markers analyzed, only EGFR was found to contribute to refining classification of patients into three risk classes with distinct OS and LRR outcomes. The addition of EGFR to three clinical parameters could identify patients having up to a fivefold difference in the risk of LRR.
Conclusions: Adding pretreatment EGFR expression data to known robust clinical prognostic variables improved the estimation of the probability for OS and LRR after radiotherapy. Its use for stratifying or selecting patients with defined tumor feature and pattern of relapse for enrollment into clinical trials testing specific therapeutic strategy warrants further investigation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bourhis J, Overgaard J, Audry H, et al. Hyperfractionated or accelerated radiotherapy in head and neck cancer: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2006;368:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Pignon J, Bourhis J, Domenge C, et al. Chemotherapy added to locoregional treatment for head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma: three meta-analyses of updated individual data. The Lancet. 2000;355:949–955. - PubMed
-
- Calais G, Alfonsi M, Bardet E, et al. Randomized trial of radiation therapy versus concomitant chemotherapy and radiation therapy for advanced-stage oropharynx carcinoma. [see comments.]. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1999;91:2081–2086. - PubMed
-
- Adelstein DJ, Li Y, Adams GL, et al. An intergroup phase III comparison of standard radiation therapy and two schedules of concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable squamous cell head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:92–98. - PubMed
-
- Forastiere AA, Goepfert H, Maor M, et al. Concurrent Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy for Organ Preservation in Advanced Laryngeal Cancer. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;349:2091–2098. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

