Leo1 subunit of the yeast paf1 complex binds RNA and contributes to complex recruitment
- PMID: 20732871
- PMCID: PMC2962465
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.140764
Leo1 subunit of the yeast paf1 complex binds RNA and contributes to complex recruitment
Abstract
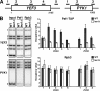
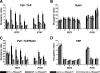
The Paf1 complex (Paf1C) affects RNA polymerase II transcription by coordinating co-transcriptional chromatin modifications and helping recruit mRNA 3' end processing factors. Paf1C cross-links to transcribed genes, but not downstream of the cleavage and polyadenylation site, suggesting that it may interact with the nascent mRNA. Paf1C purified from Saccharomyces cerevisiae binds RNA in vitro, as do the purified Leo1 and Rtf1 subunits of the complex. In vivo cross-linking and immunoprecipitation of RNA associated with Paf1C (RNA-IP) show that Leo1, but not Rtf1, is necessary for the complex to bind RNA. Cells lacking Leo1 have reduced Paf1C recruitment as well as decreased levels of histone H3 and trimethylated H3 Lys(4) within transcribed chromatin. Together, these results suggest that association of Paf1C with RNA stabilizes its localization at actively transcribed regions where it influences chromatin structure.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Separation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Paf1 complex from RNA polymerase II results in changes in its subnuclear localization.Eukaryot Cell. 2005 Jan;4(1):209-20. doi: 10.1128/EC.4.1.209-220.2005. Eukaryot Cell. 2005. PMID: 15643076 Free PMC article.
-
Small region of Rtf1 protein can substitute for complete Paf1 complex in facilitating global histone H2B ubiquitylation in yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 3;109(27):10837-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1116994109. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22699496 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal Structure of the Core Module of the Yeast Paf1 Complex.J Mol Biol. 2022 Jan 30;434(2):167369. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167369. Epub 2021 Nov 28. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34852272
-
The Paf1 complex: platform or player in RNA polymerase II transcription?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 May-Jun;1799(5-6):379-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20060942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling gene expression: a beginner's guide from chromatin modifications to mRNA export in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleus. 2025 Dec;16(1):2516909. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2025.2516909. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Nucleus. 2025. PMID: 40509867 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transmission electron microscopy for the evaluation and optimization of crystal growth.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2016 May;72(Pt 5):603-15. doi: 10.1107/S2059798316001546. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 27139624 Free PMC article.
-
The recruitment of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Paf1 complex to active genes requires a domain of Rtf1 that directly interacts with the Spt4-Spt5 complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;33(16):3259-73. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00270-13. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23775116 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple direct and indirect roles of Paf1C in elongation, splicing, and histone post-translational modifications.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 25:2024.04.25.591159. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.25.591159. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2024 Sep 24;43(9):114730. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114730. PMID: 38712269 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Cdc73 suppresses genome instability by mediating telomere homeostasis.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jan 10;14(1):e1007170. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007170. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29320491 Free PMC article.
-
Spt5 Phosphorylation and the Rtf1 Plus3 Domain Promote Rtf1 Function through Distinct Mechanisms.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Jul 14;40(15):e00150-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00150-20. Print 2020 Jul 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32366382 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

