Cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) Tethers EPAC1 in a vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-Cad)-based signaling complex and controls cAMP-mediated vascular permeability
- PMID: 20732872
- PMCID: PMC2962459
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.140004
Cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) Tethers EPAC1 in a vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-Cad)-based signaling complex and controls cAMP-mediated vascular permeability
Abstract
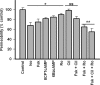
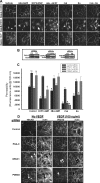
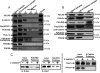
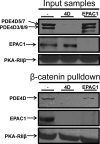
Vascular endothelial cell (VEC) permeability is largely dependent on the integrity of vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-cadherin or VE-Cad)-based intercellular adhesions. Activators of protein kinase A (PKA) or of exchange protein activated by cAMP (EPAC) reduce VEC permeability largely by stabilizing VE-Cad-based intercellular adhesions. Currently, little is known concerning the nature and composition of the signaling complexes that allow PKA or EPAC to regulate VE-Cad-based structures and through these actions control permeability. Using pharmacological, biochemical, and cell biological approaches we identified and determined the composition and functionality of a signaling complex that coordinates cAMP-mediated control of VE-Cad-based adhesions and VEC permeability. Thus, we report that PKA, EPAC1, and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) enzymes integrate into VE-Cad-based signaling complexes in human arterial endothelial cells. Importantly, we show that protein-protein interactions between EPAC1 and PDE4D serve to foster their integration into VE-Cad-based complexes and allow robust local regulation of EPAC1-based stabilization of VE-Cad-based adhesions. Of potential translational importance, we mapped the EPAC1 peptide motif involved in binding PDE4D and show that a cell-permeable variant of this peptide antagonizes EPAC1-PDE4D binding and directly alters VEC permeability. Collectively, our data indicate that PDE4D regulates both the activity and subcellular localization of EPAC1 and identify a novel mechanism for regulated EPAC1 signaling in these cells.
Figures
References
-
- Dejana E., Tournier-Lasserve E., Weinstein B. M. (2009) Dev. Cell 16, 209–221 - PubMed
-
- Vestweber D. (2008) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28, 223–232 - PubMed
-
- Galan Moya E. M., Le Guelte A., Gavard J. (2009) Cell. Signal. 21, 1727–1737 - PubMed
-
- Gavard J. (2009) FEBS Lett. 583, 1–6 - PubMed
-
- Tan W., Palmby T. R., Gavard J., Amornphimoltham P., Zheng Y., Gutkind J. S. (2008) FASEB J. 22, 1829–1838 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

