GABAergic interneuron lineages selectively sort into specific cortical layers during early postnatal development
- PMID: 20732898
- PMCID: PMC3059886
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhq155
GABAergic interneuron lineages selectively sort into specific cortical layers during early postnatal development
Abstract
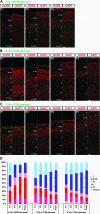
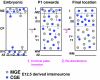
It is of considerable interest to determine how diverse subtypes of γ-aminobutyric acidergic (GABAergic) interneurons integrate into the functional network of the cerebral cortex. Using inducible in vivo genetic fate mapping approaches, we found that interneuron precursors arising from the medial ganglionic eminence (MGE) and caudal ganglionic eminence (CGE) at E12.5, respectively, populate deep and superficial cortical layers in a complementary manner in the mature cortex. These age-matched populations initiate tangential migration into the cortex simultaneously, migrate above and below the cortical plate in a similar ratio, and complete their entrance into the cortical plate by P1. Surprisingly, while these 2 interneuron populations show a comparable layer distribution at P1, they subsequently segregate into distinct cortical layers. In addition, the initiation of the radial sorting within each lineage coincided well with the upregulation of the potassium/chloride cotransporter KCC2. Moreover, layer sorting of a later born (E16.5) CGE-derived population occurred with a similar time course to the earlier born E12.5 cohorts, further suggesting that this segregation step is controlled in a subtype specific manner. We conclude that radial sorting within the early postnatal cortex is a key mechanism by which the layer-specific integration of GABAergic interneurons into the emerging cortical network is achieved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prox1 Regulates the Subtype-Specific Development of Caudal Ganglionic Eminence-Derived GABAergic Cortical Interneurons.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 16;35(37):12869-89. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1164-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26377473 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic fate mapping reveals that the caudal ganglionic eminence produces a large and diverse population of superficial cortical interneurons.J Neurosci. 2010 Feb 3;30(5):1582-94. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4515-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20130169 Free PMC article.
-
The germinal zones of the basal ganglia but not the septum generate GABAergic interneurons for the cortex.J Neurosci. 2010 Sep 8;30(36):12050-62. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6178-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20826668 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical interneurons and their origins.Neuroscientist. 2005 Jun;11(3):199-205. doi: 10.1177/1073858404270968. Neuroscientist. 2005. PMID: 15911869 Review.
-
An enhanced role and expanded developmental origins for gamma-aminobutyric acidergic interneurons in the human cerebral cortex.J Anat. 2015 Oct;227(4):384-93. doi: 10.1111/joa.12198. Epub 2014 May 20. J Anat. 2015. PMID: 24839870 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cxcr4 regulation of interneuron migration is disrupted in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 6;109(45):18601-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211507109. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23091025 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptomic and spatial organization of telencephalic GABAergic neuronal types.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 18:2024.06.18.599583. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.18.599583. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38948843 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
ZEB2 haploinsufficient Mowat-Wilson syndrome induced pluripotent stem cells show disrupted GABAergic transcriptional regulation and function.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Oct 24;15:988993. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.988993. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36353360 Free PMC article.
-
The Perineuronal Net Protein Brevican Acts in Nucleus Accumbens Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons of Adult Mice to Regulate Excitatory Synaptic Inputs and Motivated Behaviors.Biol Psychiatry. 2024 Nov 1;96(9):694-707. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2024.02.003. Epub 2024 Feb 10. Biol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38346480
-
Clonally Related GABAergic Interneurons Do Not Randomly Disperse but Frequently Form Local Clusters in the Forebrain.Neuron. 2016 Oct 5;92(1):31-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.09.033. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 27710787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angevine JB, Sidman RL. Autoradiographic study of cell migration during histogenesis of cerebral cortex in the mouse. Nature. 1961;192:766–768. - PubMed
-
- Branda CS, Dymecki SM. Talking about a revolution: the impact of site-specific recombinases on genetic analyses in mice. Dev Cell. 2004;6:7–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

