Doubles game: Src-Stat3 versus p53-PTEN in cellular migration and invasion
- PMID: 20733006
- PMCID: PMC2953057
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00004-10
Doubles game: Src-Stat3 versus p53-PTEN in cellular migration and invasion
Abstract
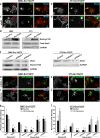
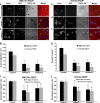
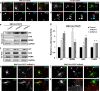
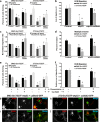
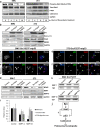
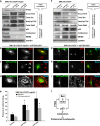
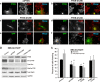
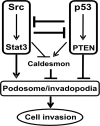
We have recently shown that Src induces the formation of podosomes and cell invasion by suppressing endogenous p53, while enhanced p53 strongly represses the Src-induced invasive phenotype. However, the mechanism by which Src and p53 play antagonistic roles in cell invasion is unknown. Here we show that the Stat3 oncogene is a required downstream effector of Src in inducing podosome structures and related invasive phenotypes. Stat3 promotes Src phenotypes through the suppression of p53 and the p53-inducible protein caldesmon, a known podosome antagonist. In contrast, enhanced p53 attenuates Stat3 function and Src-induced podosome formation by upregulating the tumor suppressor PTEN. PTEN, through the inactivation of Src/Stat3 function, also stabilizes the podosome-antagonizing p53/caldesmon axis, thereby further enhancing the anti-invasive potential of the cell. Furthermore, the protein phosphatase activity of PTEN plays a major role in the negative regulation of the Src/Stat3 pathway and represses podosome formation. Our data suggest that cellular invasiveness is dependent on the balance between two opposing forces: the proinvasive oncogenes Src-Stat3 and the anti-invasive tumor suppressors p53-PTEN.
Figures
References
-
- Artym, V. V., Y. Zhang, F. Seillier-Moiseiwitsch, K. M. Yamada, and S. C. Mueller. 2006. Dynamic interactions of cortactin and membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase at invadopodia: defining the stages of invadopodia formation and function. Cancer Res. 66:3034-3043. - PubMed
-
- Aylon, Y., and M. Oren. 2007. Living with p53, dying of p53. Cell 130:597-600. - PubMed
-
- Brisbin, S., J. Liu, J. Boudreau, J. Peng, M. Evangelista, and I. Chin-Sang. 2009. A role for C. elegans Eph RTK signaling in PTEN regulation. Dev. Cell 17:459-469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
