Sex-specific association of X-linked Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) with male systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 20733074
- PMCID: PMC2936646
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1001337107
Sex-specific association of X-linked Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) with male systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
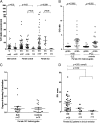
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multisystem, autoimmune disease that predominantly affects women. Previous findings that duplicated Toll-like receptor 7 (Tlr7) promotes lupus-like disease in male BXSB mice prompted us to evaluate TLR7 in human SLE. By using a candidate gene approach, we identified and replicated association of a TLR7 3'UTR SNP, rs3853839 (G/C), with SLE in 9,274 Eastern Asians (P(combined) = 6.5 x 10(-10)), with a stronger effect in male than female subjects [odds ratio, male vs. female = 2.33 (95% CI = 1.64-3.30) vs. 1.24 (95% CI = 1.14-1.34); P = 4.1 x 10(-4)]. G-allele carriers had increased TLR7 transcripts and more pronounced IFN signature than C-allele carriers; heterozygotes had 2.7-fold higher transcripts of G-allele than C-allele. These data established a functional polymorphism in type I IFN pathway gene TLR7 predisposing to SLE, especially in Chinese and Japanese male subjects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:929–939. - PubMed
-
- Yacoub Wasef SZ. Gender differences in systemic lupus erythematosus. Gend Med. 2004;1:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Gilliet M, Cao W, Liu YJ. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: Sensing nucleic acids in viral infection and autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:594–606. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, Pascual V. Type I interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Immunity. 2006;25:383–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

