Persistent expression of the full genome of hepatitis C virus in B cells induces spontaneous development of B-cell lymphomas in vivo
- PMID: 20733156
- PMCID: PMC3012587
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-05-283358
Persistent expression of the full genome of hepatitis C virus in B cells induces spontaneous development of B-cell lymphomas in vivo
Erratum in
- Blood. 2011 May 26;117(21):5782-3
Abstract
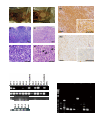
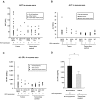
Extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection occur in 40%-70% of HCV-infected patients. B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a typical extrahepatic manifestation frequently associated with HCV infection. The mechanism by which HCV infection of B cells leads to lymphoma remains unclear. Here we established HCV transgenic mice that express the full HCV genome in B cells (RzCD19Cre mice) and observed a 25.0% incidence of diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (22.2% in males and 29.6% in females) within 600 days after birth. Expression levels of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase, as well as 32 different cytokines, chemokines and growth factors, were examined. The incidence of B-cell lymphoma was significantly correlated with only the level of soluble interleukin-2 receptor α subunit (sIL-2Rα) in RzCD19Cre mouse serum. All RzCD19Cre mice with substantially elevated serum sIL-2Rα levels (> 1000 pg/mL) developed B-cell lymphomas. Moreover, compared with tissues from control animals, the B-cell lymphoma tissues of RzCD19Cre mice expressed significantly higher levels of IL-2Rα. We show that the expression of HCV in B cells promotes non-Hodgkin-type diffuse B-cell lymphoma, and therefore, the RzCD19Cre mouse is a powerful model to study the mechanisms related to the development of HCV-associated B-cell lymphoma.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hepatitis C virus-related lymphomagenesis in a mouse model.ISRN Hematol. 2011;2011:167501. doi: 10.5402/2011/167501. Epub 2011 Jul 26. ISRN Hematol. 2011. PMID: 22084693 Free PMC article.
-
Splenic large B-cell lymphoma in patients with hepatitis C virus infection.Hum Pathol. 2005 Aug;36(8):878-85. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2005.06.005. Hum Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16112004
-
Soluble IL-2Rα facilitates IL-2-mediated immune responses and predicts reduced survival in follicular B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Blood. 2011 Sep 8;118(10):2809-20. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-340885. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21719603 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships between lymphomas linked to hepatitis C virus infection and their microenvironment.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Nov 28;19(44):7874-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.7874. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24307781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis C reactivation in patients who have diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab: a case report and review of literature.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011 Oct;11(5):379-84. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2011.04.005. Epub 2011 May 12. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011. PMID: 21729690 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue Engineering in Liver Regenerative Medicine: Insights into Novel Translational Technologies.Cells. 2020 Jan 27;9(2):304. doi: 10.3390/cells9020304. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32012725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic hepatitis C virus infection.Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2016 Feb;3(1):3-14. doi: 10.1177/2049936115585942. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26862398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Phenotype and Enhanced Antibody-Producing Ability of Peripheral B Cells in Mice with Cd19-Driven Cre Expression.Cells. 2022 Feb 16;11(4):700. doi: 10.3390/cells11040700. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35203346 Free PMC article.
-
Carcinogenic mechanisms of virus-associated lymphoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 28;15:1361009. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1361009. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38482011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Etiological factors in primary hepatic B-cell lymphoma.Virchows Arch. 2012 Apr;460(4):379-87. doi: 10.1007/s00428-012-1199-x. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Virchows Arch. 2012. PMID: 22395482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferri C, Monti M, La Civita L, et al. Infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells by hepatitis C virus in mixed cryoglobulinemia. Blood. 1993;82(12):3701–3704. - PubMed
-
- Simonetti RG, Camma C, Fiorello F, et al. Hepatitis C virus infection as a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. A case-control study. Ann Intern Med. 1992;116(2):97–102. - PubMed
-
- Silvestri F, Pipan C, Barillari G, et al. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood. 1996;87(10):4296–4301. - PubMed
-
- Ascoli V, Lo Coco F, Artini M, Levrero M, Martelli M, Negro F. Extranodal lymphomas associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Am J Clin Pathol. 1998;109(5):600–609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

