Level of albuminuria and risk of stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 20733300
- PMCID: PMC2992641
- DOI: 10.1159/000317069
Level of albuminuria and risk of stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Gross albuminuria is associated with increased stroke risk, but it is unclear whether stroke incidence varies by level of albuminuria. We meta-analyzed prospective cohort studies to investigate the impact of various albuminuria levels and continuous urinary albumin excretion (UAE) change on stroke risk.
Methods: Systematic search for studies reporting quantitative estimates of the multivariate-adjusted relative risk (RR) and 95% CI for stroke risk associated with microalbuminuria (UAE 30-300 mg/day or nearest equivalent interval) and macroalbuminuria (UAE >300 mg/day) and studies that analyzed the relation of stroke with UAE continuously. Estimates were combined using a random-effect model.
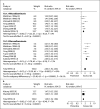
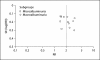
Results: We identified seven studies comprising 46,638 participants with 1,479 stroke events. Incident stroke risk was greater for macroalbuminuria (RR 2.65, 95% CI 2.25-3.14) than microalbuminuria (RR 1.58, 95% CI 1.39-1.80), a difference that was significant (p for heterogeneity < 0.001, I(2) = 96%). In addition, risk of stroke increased proportionally with rising UAE (p < 0.001), even for UAE within normal range (beginning from levels as low as 2-4 mg/g).
Conclusions: Higher albuminuria level confers greater stroke risk. These findings provide additional weight to evidence that albuminuria is strongly linked to stroke risk, and suggest that persons with elevated UAE levels may especially benefit from more intensive vascular risk reduction.
Copyright © 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Systematic review on urine albumin testing for early detection of diabetic complications.Health Technol Assess. 2005 Aug;9(30):iii-vi, xiii-163. doi: 10.3310/hta9300. Health Technol Assess. 2005. PMID: 16095545
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Antihyperthermic Treatment in the Management of Malignant Infarction of the Middle Cerebral Artery.J Clin Med. 2022 May 19;11(10):2874. doi: 10.3390/jcm11102874. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35629002 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Low Muscle Mass on Albuminuria and Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: The Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS).J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2018 Mar 2;73(3):386-392. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glx055. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 28407041 Free PMC article.
-
Higher normal ranges of urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio are independently associated with carotid intima-media thickness.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012 Sep 21;11:112. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-11-112. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012. PMID: 22995288 Free PMC article.
-
Cumulative Exposure to Systolic Blood Pressure During Young Adulthood Through Midlife and the Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio at Midlife.Am J Hypertens. 2017 May 1;30(5):502-509. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpx012. Am J Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28338726 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between resting heart rate and new-onset microalbuminuria in people with type 2 diabetes: An 8-year follow-up study.Diabet Med. 2021 May;38(5):e14436. doi: 10.1111/dme.14436. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Diabet Med. 2021. PMID: 33095935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ninomiya T, Perkovic V, Verdon C, Barzi F, Cass A, Gallagher M, Jardine M, Anderson C, Chalmers J, Craig JC, Huxley R. Proteinuria and stroke: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:417–425. - PubMed
-
- Ovbiagele B. Microalbuminuria: risk factor and potential therapeutic target for stroke? J Neurol Sci. 2008;271:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, Moher D, Becker BJ, Sipe TA, Thacker SB. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (moose) group. JAMA. 2000;283:2008–2012. - PubMed
-
- Miettinen H, Haffner SM, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, Pyorala K, Laakso M. Proteinuria predicts stroke and other atherosclerotic vascular disease events in nondiabetic and non-insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. Stroke. 1996;27:2033–2039. - PubMed
-
- Valmadrid CT, Klein R, Moss SE, Klein BE. The risk of cardiovascular disease mortality associated with microalbuminuria and gross proteinuria in persons with older-onset diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:1093–1100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

