Rosiglitazone monotherapy in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease: results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III study
- PMID: 20733306
- PMCID: PMC3214882
- DOI: 10.1159/000318845
Rosiglitazone monotherapy in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease: results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III study
Abstract
Background/aims: A phase II study of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ agonist rosiglitazone extended release (RSG XR) in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease (AD) detected a treatment benefit to cognition in apolipoprotein E(APOE)-ε4-negative subjects. The current phase III study with prospective stratification by APOE genotype was conducted to confirm the efficacy and safety of RSG XR in mild-to-moderate AD. An open-label extension study assessed the long-term safety and tolerability of 8 mg RSG XR.
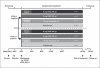
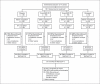
Methods: This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study enrolled 693 subjects. Within 2 APOE allelic strata (ε4-positive, ε4-negative), subjects were randomized (2:2:2:1) to once-daily placebo, 2 mg RSG XR, 8 mg RSG XR or 10 mg donepezil (control). Coprimary endpoints were change from baseline to week 24 in the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-cognitive subscale (ADAS-Cog) score, and week 24 Clinician's Interview-Based Impression of Change plus caregiver input (CIBIC+).
Results: At week 24, no significant differences from placebo in change from baseline in coprimary endpoints were detected with either the RSG XR dose in APOE-ε4-negative subjects or overall. For donepezil, no significant treatment difference was detected in ADAS-Cog; however, a significant difference was detected (p = 0.009) on the CIBIC+. Peripheral edema was the most common adverse event for 8 mg RSG XR (15%) and placebo (5%), and nasopharyngitis for 2 mg RSG XR (7%).
Conclusion: No evidence of efficacy of 2 mg or 8 mg RSG XR monotherapy in cognition or global function was detected in the APOE-ε4-negative or other analysis populations. The safety and tolerability of RSG XR was consistent with its known pharmacology.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00428090 NCT00550420.
Copyright © 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures


References
-
- Cummings JL. Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:56–67. - PubMed
-
- Watson GS, Craft S. The role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: implications for treatment. CNS Drugs. 2003;17:27–45. - PubMed
-
- Craft S. Insulin resistance and Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis: potential mechanisms and implications for treatment. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007;4:147–152. - PubMed
-
- Profenno LA, Porsteinsson AP, Faraone SV. Meta-analysis of Alzheimer's disease risk with obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67:505–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

