Efficacy of bladder-preserving therapy for patients with t3b, t4a, and t4b transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder
- PMID: 20733957
- PMCID: PMC2924555
- DOI: 10.4111/kju.2010.51.8.525
Efficacy of bladder-preserving therapy for patients with t3b, t4a, and t4b transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder
Abstract
Purpose: Radical cystectomy has been the most widely used method in the treatment of bladder cancer, but it is limited by major problems. Therefore, we investigated the results of bladder-preserving treatment in patients with T3b, T4a, and T4b transitional carcinoma of the bladder who underwent transurethral resection of bladder cancer and subsequent administration of chemotherapy.
Materials and methods: Of all patients who were diagnosed with bladder cancer and underwent bladder-preserving treatment between January 2001 and August 2008, 78 patients with at least 12 months of follow-up data were enrolled in this study. All patients received gemcitabine (1,000 mg/m(2)) and cisplatin (70 mg/m(2)) once per month postoperatively for a total of 6 months and completed a follow-up visit every 3 months. The patient survival rate and prognostic factors (age, tumor size, differentiation, number of lesions, stage, and presence of hydronephrosis) were assessed. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to analyze survival rate, and Cox multiple regression analysis was used for prognostic factors.
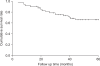
Results: The mean patient age was 68.32+/-8.6 years, the mean duration of follow-up was 54.70+/-32.8 months, and the median duration of follow-up was 49.0 months. The 5-year survival rate was 66.2%. Single lesions were found in 28 cases (35.9%), and multiple lesions were found in 50 cases (64.1%). Stage T3b lesions were identified in 56 cases (71.8%), stage T4a lesions were identified in 16 cases (20.5%), and stage T4b lesions were identified in 6 cases (7.7%). Tumor size was less than 4 cm in 4 cases (59.0%) and greater than 4 cm in 32 (41.0%). Hydronephrosis was present in 21 cases (26.9%). In the 5-year survival analysis, prognostic factors significantly influencing survival rate were T-stage of the tumor and absence of hydronephrosis and complete regression after treatment (p<0.05). Multivariate analysis revealed that tumor stage and the absence of hydronephrosis were statistically significant prognostic indicators.
Conclusions: In patients with T3b, T4a, and T4b transitional carcinoma of the bladder, bladder preservation may prevent a decrease in quality of life. Also, our findings suggest that this approach could be considered a primary treatment option for patients with T3b stage tumors without evidence of hydronephrosis.
Keywords: Drug therapy; Therapeutics; Urinary bladder neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conservative treatment with transurethral resection, neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by radiochemotherapy in stage T2-3 transitional bladder cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2006 Dec;8(12):903-11. doi: 10.1007/s12094-006-0154-1. Clin Transl Oncol. 2006. PMID: 17169764 Clinical Trial.
-
Concurrent cisplatin and radiotherapy for patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer who are not candidates for radical cystectomy.J Urol. 1996 Oct;156(4):1258-62. J Urol. 1996. PMID: 8808849 Clinical Trial.
-
[Results of long-term treatment of inoperable cancer of the bladder with cisplatin and concurrent irradiation: prognostic factors of local control and survival].Cancer Radiother. 1998 Apr;2 Suppl 1:85s-91s. Cancer Radiother. 1998. PMID: 9749086 Clinical Trial. French.
-
Combined-modality therapy for bladder cancer.Oncology (Williston Park). 1997 Sep;11(9 Suppl 9):18-26. Oncology (Williston Park). 1997. PMID: 9330404 Review.
-
Radiotherapy for stage T3b transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder.Semin Urol Oncol. 1996 May;14(2):86-95. Semin Urol Oncol. 1996. PMID: 8734736 Review.
Cited by
-
Does radical cystectomy improve overall survival in octogenarians with muscle-invasive bladder cancer?Korean J Urol. 2011 Jul;52(7):446-51. doi: 10.4111/kju.2011.52.7.446. Epub 2011 Jul 24. Korean J Urol. 2011. PMID: 21860763 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in the Use of Chemotherapy before and after Radical Cystectomy in Patients with Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer in Korea.J Korean Med Sci. 2015 Aug;30(8):1150-6. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.8.1150. Epub 2015 Jul 15. J Korean Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26240494 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Solsona E, Iborra I, Ricos JV, Monros JL, Casanova J, Calabuig C. Feasibility of transurethral resection for muscle infiltrating carcinoma of the bladder: long-term followup of a prospective study. J Urol. 1998;159:95–98. - PubMed
-
- Herr HW. Transurethral resection of muscle-invasive bladder cancer: 10-year outcome. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:89–93. - PubMed
-
- Shipley WU, Kaufman DS, Zehr E, Heney NM, Lane SC, Thakral HK, et al. Selective bladder preservation by combined modality protocol treatment: long-term outcomes of 190 patients with invasive bladder cancer. Urology. 2002;60:62–67. - PubMed
-
- Mottet N, Castagnola C, Rischmann P, Deixonne M, Guyot M, Coloby P, et al. Quality of life after cystectomy: French national survey conducted by the French Association of Urology (AFU), the French Federation of Stoma Patients (FSF) and the French Association of Enterostomy Patients (AFET) in patients with ileal conduit urinary diversion or orthotopic neobladder. Prog Urol. 2008;18:292–298. - PubMed
-
- Hart S, Skinner EC, Meyerowitz BE, Boyd S, Lieskovsky G, Skinner DG. Quality of life after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer in patients with an ileal conduit, cutaneous or urethral kock pouch. J Urol. 1999;162:77–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources