Serine residue 115 of MAPK-activated protein kinase MK5 is crucial for its PKA-regulated nuclear export and biological function
- PMID: 20734105
- PMCID: PMC3037495
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0496-2
Serine residue 115 of MAPK-activated protein kinase MK5 is crucial for its PKA-regulated nuclear export and biological function
Abstract
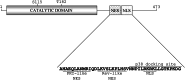
The mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase-5 (MK5) resides predominantly in the nucleus of resting cells, but p38(MAPK), extracellular signal-regulated kinases-3 and -4 (ERK3 and ERK4), and protein kinase A (PKA) induce nucleocytoplasmic redistribution of MK5. The mechanism by which PKA causes nuclear export remains unsolved. In the study reported here we demonstrated that Ser-115 is an in vitro PKA phosphoacceptor site, and that PKA, but not p38(MAPK), ERK3 or ERK4, is unable to redistribute MK5 S115A to the cytoplasm. However, the phospho-mimicking MK5 S115D mutant resides in the cytoplasm in untreated cells. While p38(MAPK), ERK3 and ERK4 fail to trigger nuclear export of the kinase dead T182A and K51E MK5 mutants, S115D/T182A and K51E/S115D mutants were able to enter the cytoplasm of resting cells. Finally, we demonstrated that mutations in Ser-115 affect the biological properties of MK5. Taken together, our results suggest that Ser-115 plays an essential role in PKA-regulated nuclear export of MK5, and that it also may regulate the biological functions of MK5.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Ser(186) phospho-acceptor site within ERK4 is essential for its ability to interact with and activate PRAK/MK5.Biochem J. 2008 May 1;411(3):613-22. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071369. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18248330
-
Regulation of MAPK-activated protein kinase 5 activity and subcellular localization by the atypical MAPK ERK4/MAPK4.J Biol Chem. 2006 Nov 17;281(46):35499-510. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M606225200. Epub 2006 Sep 13. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16971392
-
Both binding and activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) play essential roles in regulation of the nucleocytoplasmic distribution of MAPK-activated protein kinase 5 by cellular stress.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Oct;22(20):6931-45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.20.6931-6945.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12242275 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the activation, interaction partners and possible functions of MK5/PRAK.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016 Jan 1;21(2):374-84. doi: 10.2741/4394. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016. PMID: 26709779 Review.
-
MK5: A novel regulator of cardiac fibroblast function?IUBMB Life. 2017 Oct;69(10):785-794. doi: 10.1002/iub.1677. Epub 2017 Sep 11. IUBMB Life. 2017. PMID: 28941148 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of hsp27 kinases activated by elevated aortic pressure in heart.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Dec;371(1-2):31-42. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1420-x. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22878564 Free PMC article.
-
The adrenergic-induced ERK3 pathway drives lipolysis and suppresses energy dissipation.Genes Dev. 2020 Apr 1;34(7-8):495-510. doi: 10.1101/gad.333617.119. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 32139423 Free PMC article.
-
Homology modeling and ligand docking of Mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 5 (MK5).Theor Biol Med Model. 2013 Sep 14;10:56. doi: 10.1186/1742-4682-10-56. Theor Biol Med Model. 2013. PMID: 24034446 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative molecular dynamics simulations of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 5.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Mar 19;15(3):4878-902. doi: 10.3390/ijms15034878. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24651460 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological roles of mitogen-activated-protein-kinase-activated p38-regulated/activated protein kinase.World J Biol Chem. 2011 May 26;2(5):73-89. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v2.i5.73. World J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21666810 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

