Longitudinal association of HIV conspiracy beliefs with sexual risk among black males living with HIV
- PMID: 20734227
- PMCID: PMC3029491
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-010-9796-7
Longitudinal association of HIV conspiracy beliefs with sexual risk among black males living with HIV
Abstract
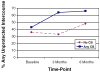
Research is needed to identify culturally relevant factors that may contribute to sexual risk among African Americans. We investigated HIV-specific medical mistrust as one such cultural factor, often exhibited as conspiracy beliefs about HIV (e.g., "AIDS was produced in a government laboratory"), which may be indicative of general suspicion of HIV treatment and prevention messages. Over a 6-month time-period, we measured endorsement of HIV conspiracy beliefs three times and frequency of condom use monthly among 181 HIV-positive African American males. A hierarchical multivariate repeated-measures logistic random effects model indicated that greater belief in HIV conspiracies was associated with a higher likelihood of reporting unprotected intercourse across all time-points. An average of 54% of participants who endorsed conspiracies reported unprotected intercourse, versus 39% who did not endorse conspiracies. Secondary prevention interventions may need to address medical mistrust as a contributor to sexual risk among African Americans living with HIV.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Medical mistrust among social network members may contribute to antiretroviral treatment nonadherence in African Americans living with HIV.Soc Sci Med. 2016 Sep;164:133-140. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2016.03.028. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Soc Sci Med. 2016. PMID: 27046475 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of African Americans' sociodemographic characteristics to belief in conspiracies about HIV/AIDS and birth control.J Natl Med Assoc. 2006 Jul;98(7):1144-50. J Natl Med Assoc. 2006. PMID: 16895286 Free PMC article.
-
The Health and Sociocultural Correlates of AIDS Genocidal Beliefs and Medical Mistrust Among African American MSM.AIDS Behav. 2018 Jun;22(6):1814-1825. doi: 10.1007/s10461-016-1657-6. AIDS Behav. 2018. PMID: 28013400 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the relationship of conspiracy beliefs about HIV/AIDS to sexual behaviors and attitudes among African-American adults.J Natl Med Assoc. 2003 Nov;95(11):1057-65. J Natl Med Assoc. 2003. PMID: 14651372 Free PMC article.
-
Are HIV/AIDS conspiracy beliefs a barrier to HIV prevention among African Americans?J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005 Feb 1;38(2):213-8. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200502010-00014. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005. PMID: 15671808
Cited by
-
Medical mistrust among social network members may contribute to antiretroviral treatment nonadherence in African Americans living with HIV.Soc Sci Med. 2016 Sep;164:133-140. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2016.03.028. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Soc Sci Med. 2016. PMID: 27046475 Free PMC article.
-
Health care and HIV testing experiences among Black men in the South: implications for "Seek, Test, Treat, and Retain" HIV prevention strategies.AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2013 Feb;27(2):123-33. doi: 10.1089/apc.2012.0269. Epub 2012 Dec 26. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2013. PMID: 23268586 Free PMC article.
-
Association of discrimination-related trauma with sexual risk among HIV-positive African American men who have sex with men.Am J Public Health. 2013 May;103(5):875-80. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2012.300951. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Am J Public Health. 2013. PMID: 23488499 Free PMC article.
-
Towards a More Inclusive and Dynamic Understanding of Medical Mistrust Informed by Science.Behav Med. 2019 Apr-Jun;45(2):79-85. doi: 10.1080/08964289.2019.1619511. Behav Med. 2019. PMID: 31343962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Longitudinal Analysis of Treatment Optimism and HIV Acquisition and Transmission Risk Behaviors Among Black Men Who Have Sex with Men in HPTN 061.AIDS Behav. 2017 Oct;21(10):2958-2972. doi: 10.1007/s10461-017-1756-z. AIDS Behav. 2017. PMID: 28352984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV and AIDS in the United States: a picture of today’s epidemic. 2008. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/topics/surveillance/united_states.htm.
-
- Mitsch A, Hu X, Harrison KM, Durant T. Trends in HIV/AIDS diagnoses among men who have sex with men–33 states, 2001–2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008;57(25):681–6. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Subpopulation estimates from the HIV incidence surveillance system–United States, 2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008;57(36):985–9. - PubMed
-
- Sifakis F, Flynn CP, Metsch LR, LaLota M, Murrill C, Koblin BA, et al. HIV prevalence, unrecognized infection, and HIV testing among men who have sex with men–five US cities, June 2004-April 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2005;54(24):597–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical