Development of anxiety: the role of threat appraisal and fear learning
- PMID: 20734364
- PMCID: PMC2995000
- DOI: 10.1002/da.20733
Development of anxiety: the role of threat appraisal and fear learning
Abstract
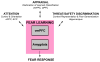
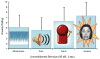
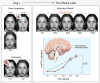
Anxious individuals exhibit threat biases at multiple levels of information processing. From a developmental perspective, abnormal safety learning in childhood may establish threat-related appraisal biases early, which may contribute to chronic disorders in adulthood. This review illustrates how the interface among attention, threat appraisal, and fear learning can generate novel insights for outcome prediction. This review summarizes data on amygdala function, as it relates to learning and attention, highlights the importance of examining threat appraisal, and introduces a novel imaging paradigm to investigate the neural correlates of threat appraisal and threat-sensitivity during extinction recall. This novel paradigm can be used to investigate key questions relevant to prognosis and treatment. Depression and Anxiety, 2011.© 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
© 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amygdala-Cortical Connectivity: Associations with Anxiety, Development, and Threat.Depress Anxiety. 2016 Oct;33(10):917-926. doi: 10.1002/da.22470. Depress Anxiety. 2016. PMID: 27699940 Free PMC article.
-
Response to learned threat: An FMRI study in adolescent and adult anxiety.Am J Psychiatry. 2013 Oct;170(10):1195-204. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12050651. Am J Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23929092 Free PMC article.
-
Skin Conductance Responses and Neural Activations During Fear Conditioning and Extinction Recall Across Anxiety Disorders.JAMA Psychiatry. 2017 Jun 1;74(6):622-631. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.0329. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28403387 Free PMC article.
-
Neurocognitive mechanisms of anxiety: an integrative account.Trends Cogn Sci. 2007 Jul;11(7):307-16. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2007.05.008. Epub 2007 Jun 5. Trends Cogn Sci. 2007. PMID: 17553730 Review.
-
Extending animal models of fear conditioning to humans.Biol Psychol. 2006 Jul;73(1):39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2006.01.006. Epub 2006 Feb 10. Biol Psychol. 2006. PMID: 16472906 Review.
Cited by
-
FKBP5 and attention bias for threat: associations with hippocampal function and shape.JAMA Psychiatry. 2013 Apr;70(4):392-400. doi: 10.1001/2013.jamapsychiatry.210. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23407841 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Instructional Cognitive Load in the Context of Students' Psychological Challenge and Threat Orientations: A Multi-Level Latent Profile Analysis of Students and Classrooms.Front Psychol. 2021 Jul 1;12:656994. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.656994. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34276480 Free PMC article.
-
Test-retest reliability of approach-avoidance conflict decision-making during functional magnetic resonance imaging in healthy adults.Hum Brain Mapp. 2021 Jun 1;42(8):2347-2361. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25371. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021. PMID: 33650761 Free PMC article.
-
Traits of fear resistance and susceptibility in an advanced intercross line.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Nov;38(9):3314-24. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12337. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23968228 Free PMC article.
-
Linked networks for learning and expressing location-specific threat.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jan 30;115(5):E1032-E1040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1714691115. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29326231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beesdo K, Bittner A, Pine DS, et al. Incidence of social anxiety disorder and the consistent risk for secondary depression in the first three decades of life. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64(8):903–12. - PubMed
-
- Pine DS, Cohen P, Gurley D, et al. The risk for early-adulthood anxiety and depressive disorders in adolescents with anxiety and depressive disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55(1):56–64. - PubMed
-
- Gregory AM, Caspi A, Moffitt TE, et al. Juvenile mental health histories of adults with anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(2):301–8. - PubMed
-
- Stein MB, Fuetsch M, Muller N, et al. Social anxiety disorder and the risk of depression: a prospective community study of adolescents and young adults. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58(3):251–6. - PubMed
-
- Pine DS. Research review: a neuroscience framework for pediatric anxiety disorders. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2007;48(7):631–48. - PubMed

