Structural determinants in the second intracellular loop of the human cannabinoid CB1 receptor mediate selective coupling to G(s) and G(i)
- PMID: 20735408
- PMCID: PMC3010585
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01006.x
Structural determinants in the second intracellular loop of the human cannabinoid CB1 receptor mediate selective coupling to G(s) and G(i)
Abstract
Background and purpose: The cannabinoid CB(1) receptor is primarily thought to be functionally coupled to the G(i) form of G proteins, through which it negatively regulates cAMP accumulation. Here, we investigated the dual coupling properties of CB(1) receptors and characterized the structural determinants that mediate selective coupling to G(s) and G(i).
Experimental approach: A cAMP-response element reporter gene system was employed to quantitatively analyze cAMP change. CB(1)/CB(2) receptor chimeras and site-directed mutagenesis combined with functional assays and computer modelling were used to determine the structural determinants mediating selective coupling to G(s) and G(i).
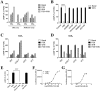
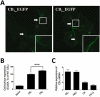
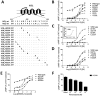
Key results: CB(1) receptors could couple to both G(s)-mediated cAMP accumulation and G(i)-induced activation of ERK1/2 and Ca(2+) mobilization, whereas CB(2) receptors selectively coupled to G(i) and inhibited cAMP production. Using CB(1)/CB(2) chimeric receptors, the second intracellular loop (ICL2) of the CB(1) receptor was identified as primarily responsible for mediating G(s) and G(i) coupling specificity. Furthermore, mutation of Leu-222 in ICL2 to either Ala or Pro switched G protein coupling from G(s) to G(i), while to Ile or Val led to balanced coupling of the mutant receptor with G(s) and G(i) .
Conclusions and implications: The ICL2 of CB(1) receptors and in particular Leu-222, which resides within a highly conserved DRY(X)(5) PL motif, played a critical role in G(s) and G(i) protein coupling and specificity. Our studies provide new insight into the mechanisms governing the coupling of CB(1) receptors to G proteins and cannabinoid-induced tolerance.
© 2010 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2010 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

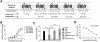


Similar articles
-
The second intracellular loop of the human cannabinoid CB2 receptor governs G protein coupling in coordination with the carboxyl terminal domain.PLoS One. 2013 May 7;8(5):e63262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063262. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23667597 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo pharmacology of synthetic olivetol- or resorcinol-derived cannabinoid receptor ligands.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Oct;149(4):431-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706888. Epub 2006 Sep 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16953186 Free PMC article.
-
Differential coupling of beta3A- and beta3B-adrenergic receptors to endogenous and chimeric Galphas and Galphai.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Oct;291(4):E704-15. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00048.2006. Epub 2006 May 16. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16705062
-
CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor binding studies based on modeling and mutagenesis approaches.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005 Jul;5(7):651-8. doi: 10.2174/1389557054368754. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16026311 Review.
-
Structural Insights into CB1 Receptor Biased Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 13;20(8):1837. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081837. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31013934 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of a Signaling Cannabinoid Receptor 1-G Protein Complex.Cell. 2019 Jan 24;176(3):448-458.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.040. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Cell. 2019. PMID: 30639101 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3 interaction with Gq.Commun Biol. 2024 Mar 23;7(1):362. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06056-1. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38521872 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Endocannabinoid System Targeting for Improved Specificity: Strategic Approaches to Targeted Drug Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 30;23(21):13223. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113223. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bombyx adipokinetic hormone receptor activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 via G protein-dependent PKA and PKC but β-arrestin-independent pathways.Biochemistry. 2010 Dec 28;49(51):10862-72. doi: 10.1021/bi1014425. Epub 2010 Dec 2. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 21126059 Free PMC article.
-
On the G protein-coupling selectivity of the native A2B adenosine receptor.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 May;151:201-213. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.003. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29225130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abadji V, Lucas-Lenard JM, Chin C, Kendall DA. Involvement of the carboxyl terminus of the third intracellular loop of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor in constitutive activation of Gs. J Neurochem. 1999;72:2032–2038. - PubMed
-
- Adams IB, Martin BR. Cannabis: pharmacology and toxicology in animals and humans. Addiction. 1996;91:1585–1614. - PubMed
-
- Allgeier A, Laugwitz KL, Van Sande J, Schultz G, Dumont JE. Multiple G-protein coupling of the dog thyrotropin receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997;127:81–90. - PubMed
-
- Anavi-Goffer S, Fleischer D, Hurst DP, Lynch DL, Barnett-Norris J, Shi S, et al. Helix 8 Leu in the CB1 cannabinoid receptor contributes to selective signal transduction mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:25100–25113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

