Structural determinants in the second intracellular loop of the human cannabinoid CB1 receptor mediate selective coupling to G(s) and G(i)
- PMID: 20735408
- PMCID: PMC3010585
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01006.x
Structural determinants in the second intracellular loop of the human cannabinoid CB1 receptor mediate selective coupling to G(s) and G(i)
Abstract
Background and purpose: The cannabinoid CB(1) receptor is primarily thought to be functionally coupled to the G(i) form of G proteins, through which it negatively regulates cAMP accumulation. Here, we investigated the dual coupling properties of CB(1) receptors and characterized the structural determinants that mediate selective coupling to G(s) and G(i).
Experimental approach: A cAMP-response element reporter gene system was employed to quantitatively analyze cAMP change. CB(1)/CB(2) receptor chimeras and site-directed mutagenesis combined with functional assays and computer modelling were used to determine the structural determinants mediating selective coupling to G(s) and G(i).
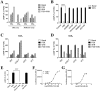
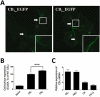
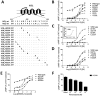
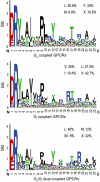
Key results: CB(1) receptors could couple to both G(s)-mediated cAMP accumulation and G(i)-induced activation of ERK1/2 and Ca(2+) mobilization, whereas CB(2) receptors selectively coupled to G(i) and inhibited cAMP production. Using CB(1)/CB(2) chimeric receptors, the second intracellular loop (ICL2) of the CB(1) receptor was identified as primarily responsible for mediating G(s) and G(i) coupling specificity. Furthermore, mutation of Leu-222 in ICL2 to either Ala or Pro switched G protein coupling from G(s) to G(i), while to Ile or Val led to balanced coupling of the mutant receptor with G(s) and G(i) .
Conclusions and implications: The ICL2 of CB(1) receptors and in particular Leu-222, which resides within a highly conserved DRY(X)(5) PL motif, played a critical role in G(s) and G(i) protein coupling and specificity. Our studies provide new insight into the mechanisms governing the coupling of CB(1) receptors to G proteins and cannabinoid-induced tolerance.
© 2010 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2010 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

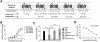


References
-
- Abadji V, Lucas-Lenard JM, Chin C, Kendall DA. Involvement of the carboxyl terminus of the third intracellular loop of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor in constitutive activation of Gs. J Neurochem. 1999;72:2032–2038. - PubMed
-
- Adams IB, Martin BR. Cannabis: pharmacology and toxicology in animals and humans. Addiction. 1996;91:1585–1614. - PubMed
-
- Allgeier A, Laugwitz KL, Van Sande J, Schultz G, Dumont JE. Multiple G-protein coupling of the dog thyrotropin receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997;127:81–90. - PubMed
-
- Anavi-Goffer S, Fleischer D, Hurst DP, Lynch DL, Barnett-Norris J, Shi S, et al. Helix 8 Leu in the CB1 cannabinoid receptor contributes to selective signal transduction mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:25100–25113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

