Insulin resistance in penile arteries from a rat model of metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 20735420
- PMCID: PMC2989587
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00825.x
Insulin resistance in penile arteries from a rat model of metabolic syndrome
Abstract
Background and purpose: Metabolic and cardiovascular abnormalities accompanying metabolic syndrome, such as obesity, insulin resistance and hypertension, are all associated with endothelial dysfunction and are independent risk factors for erectile dysfunction. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the vascular effects of insulin in penile arteries and whether these effects are impaired in a rat model of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.
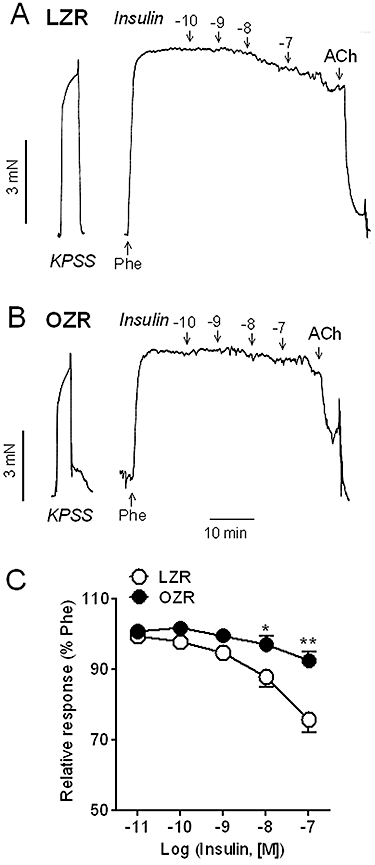
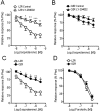
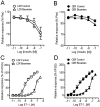
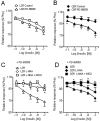
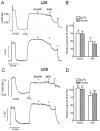
Experimental approach: Penile arteries from obese Zucker rats (OZR) and their counterpart, lean Zucker rats (LZR), were mounted on microvascular myographs and the effects of insulin were assessed in the absence and presence of endothelium and of specific inhibitors of nitric oxide (NO) synthesis, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Insulin-induced changes in intracellular Ca(2+) concentration [Ca(2+)](i) were also examined. KEY RESULTS OZR exhibited mild hyperglycaemia, hypercholesterolemia, hypertryglyceridemia and hyperinsulinemia. Insulin induced endothelium- and NO-dependent relaxations in LZR that were impaired in OZR. Inhibition of PI3K reduced relaxation induced by insulin and by the beta-adrenoceptor agonist isoprenaline, mainly in arteries from LZR. Antagonism of endothelin 1 (ET-1) receptors did not alter insulin-induced relaxation in either LZR or OZR, but MAPK blockade increased the responses in OZR. Insulin decreased [Ca(2+)](i), a response impaired in OZR.
Conclusions and implications: Insulin-induced relaxation was impaired in penile arteries of OZR due to altered NO release through the PI3K pathway and unmasking of a MAPK-mediated vasoconstriction. This vascular insulin resistance is likely to contribute to the endothelial dysfunction and erectile dysfunction associated with insulin resistant states.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of neural NO synthase (nNOS) uncoupling in the dysfunctional nitrergic vasorelaxation of penile arteries from insulin-resistant obese Zucker rats.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e36027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036027. Epub 2012 Apr 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22540017 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-1 contributes to endothelial dysfunction and enhanced vasoconstriction through augmented superoxide production in penile arteries from insulin-resistant obese rats: role of ET(A) and ET(B) receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;171(24):5682-95. doi: 10.1111/bph.12870. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25091502 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired endothelin calcium signaling coupled to endothelin type B receptors in penile arteries from insulin-resistant obese Zucker rats.J Sex Med. 2013 Sep;10(9):2141-53. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12234. Epub 2013 Jul 22. J Sex Med. 2013. PMID: 23875673
-
Physiological regulation of penile arteries and veins.Int J Impot Res. 2008 Jan-Feb;20(1):17-29. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3901581. Epub 2007 Jul 19. Int J Impot Res. 2008. PMID: 17637789 Review.
-
The Zucker rat model of obesity, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia, and renal injury.Hypertension. 1992 Jan;19(1 Suppl):I110-5. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.19.1_suppl.i110. Hypertension. 1992. PMID: 1730447 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of neural NO synthase (nNOS) uncoupling in the dysfunctional nitrergic vasorelaxation of penile arteries from insulin-resistant obese Zucker rats.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e36027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036027. Epub 2012 Apr 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22540017 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of metformin on endothelial health and erectile dysfunction.Transl Androl Urol. 2017 Jun;6(3):556-565. doi: 10.21037/tau.2017.03.52. Transl Androl Urol. 2017. PMID: 28725599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin relaxes bladder via PI3K/AKT/eNOS pathway activation in mucosa: unfolded protein response-dependent insulin resistance as a cause of obesity-associated overactive bladder.J Physiol. 2013 May 1;591(9):2259-73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.251843. Epub 2013 Mar 11. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23478138 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-1 contributes to endothelial dysfunction and enhanced vasoconstriction through augmented superoxide production in penile arteries from insulin-resistant obese rats: role of ET(A) and ET(B) receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;171(24):5682-95. doi: 10.1111/bph.12870. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25091502 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K), Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK), and Protein Kinase C (PKC) in Calcium Signaling Pathways Linked to the α1-Adrenoceptor in Resistance Arteries.Front Physiol. 2019 Feb 6;10:55. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00055. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30787881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baron AD, Laakso M, Brechtel G, Edelman SV. Mechanism of insulin resistance in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a major role for reduced skeletal muscle blood flow. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991;73:637–643. - PubMed
-
- Begum N, Sandu OA, Duddy N. Negative regulation of rho signaling by insulin and its impact on actin cytoskeleton organization in vascular smooth muscle cells: role of nitric oxide and cyclic guanosine monophosphate signaling pathways. Diabetes. 2002;51:2256–2263. - PubMed
-
- Cardillo C, Nambi SS, Kilcoyne CM, Choucair WK, Katz A, Quon MJ, et al. Insulin stimulates both endothelin and nitric oxide activity in the human forearm. Circulation. 1999;100:820–825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

