Protective effect of hydrogen sulphide against 6-OHDA-induced cell injury in SH-SY5Y cells involves PKC/PI3K/Akt pathway
- PMID: 20735429
- PMCID: PMC2989596
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00887.x
Protective effect of hydrogen sulphide against 6-OHDA-induced cell injury in SH-SY5Y cells involves PKC/PI3K/Akt pathway
Erratum in
- Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;168(8):2011-2
Abstract
Background and purpose: Hydrogen sulphide (H(2)S) is a novel neuromodulator. The present study aimed to investigate the protective effect of H(2)S against cell injury induced by 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), a selective dopaminergic neurotoxin often used to establish a model of Parkinson's disease for studying the underlying mechanisms of this condition.
Experimental approach: Cell viability in SH-SY5Y cells was measured using MTT assay. Western blot analysis and pharmacological manipulation were employed to study the signalling mechanisms.
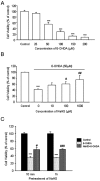
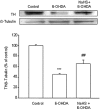
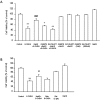
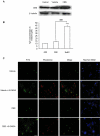
Key results: Treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with 6-OHDA (50-200 microM) for 12 h decreased cell viability. Exogenous application of NaHS (an H(2)S donor, 100-1000 microM) or overexpression of cystathionine beta-synthase (a predominant enzyme to produce endogenous H(2)S in SH-SY5Y cells) protected cells against 6-OHDA-induced cell apoptosis and death. Furthermore, NaHS reversed 6-OHDA-induced loss of tyrosine hydroxylase. Western blot analysis showed that NaHS reversed the down-regulation of PKCalpha, epsilon and Akt and the up-regulation of PKCdelta in 6-OHDA-treated cells. Blockade of PKCalpha with Gö6976 (2 microM), PKCepsilon with EAVSLKPT (200 microM) or PI3K with LY294002 (20 microM) reduced the protective effects of H(2)S. However, inhibition of PKCdelta with rottlerin (5 microM) failed to affect 6-OHDA-induced cell injury. These data suggest that the protective effects of NaHS mainly resulted from activation of PKCalpha, epsilon and PI3K/Akt pathway. In addition, NaHS-induced Akt phosphorylation was significantly attenuated by Gö6976 and EAVSLKPT, suggesting that the activation of Akt by NaHS is PKCalpha, epsilon-dependent.
Conclusions and implications: H(2)S protects SH-SY5Y cells against 6-OHDA-induced cell injury by activating the PKCalpha, epsilon/PI3K/Akt pathway.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hydrogen sulfide protects SH-SY5Y cells against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Jul 1;303(1):C81-91. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00281.2011. Epub 2012 May 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22555844
-
Isorhamnetin ameliorates dopaminergic neuronal damage via targeting FOSL1 to activate AKT/mTOR in 6-OHDA-induced SH-SY5Y cells.J Neurophysiol. 2025 Jan 1;133(1):22-33. doi: 10.1152/jn.00351.2024. Epub 2024 Nov 19. J Neurophysiol. 2025. PMID: 39560297
-
Protective Effects of Fisetin Against 6-OHDA-Induced Apoptosis by Activation of PI3K-Akt Signaling in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells.Neurochem Res. 2018 Feb;43(2):488-499. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2445-z. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29204750
-
Orexin-A Protects Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells Against 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurotoxicity: Involvement of PKC and PI3K Signaling Pathways.Rejuvenation Res. 2017 Apr;20(2):125-133. doi: 10.1089/rej.2016.1836. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Rejuvenation Res. 2017. PMID: 27814668
-
Chronic neuroprotective effects of low concentration lithium on SH-SY5Y cells: possible involvement of stress proteins and gene expression.Neural Regen Res. 2014 Apr 1;9(7):735-40. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.131578. Neural Regen Res. 2014. PMID: 25206881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of theaflavins on neuron against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2012 Mar;50(2):133-8. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.11-28. Epub 2011 Sep 13. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22448094 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Oncological and Non-Oncological Disorders and Its Regulation by Non-Coding RNAs: A Comprehensive Review.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Jan 18;10(1):7. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10010007. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 38250807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotection of SAK3 on scopolamine-induced cholinergic dysfunction in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.Cytotechnology. 2020 Feb;72(1):155-164. doi: 10.1007/s10616-019-00366-7. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Cytotechnology. 2020. PMID: 31933104 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteine Metabolism in Neuronal Redox Homeostasis.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018 May;39(5):513-524. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.02.007. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29530337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PKCδ inhibition enhances tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation in mice after methamphetamine treatment.Neurochem Int. 2011 Aug;59(1):39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.03.022. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Neurochem Int. 2011. PMID: 21672585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abad F, Maroto R, Lopez MG, Sanchez-Garcia P, Garcia AG. Pharmacological protection against the cytotoxicity induced by 6-hydroxydopamine and H2O2 in chromaffin cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;293:55–64. - PubMed
-
- Akao Y, Maruyama W, Yi H, Shamoto-Nagai M, Youdim MB, Naoi M. An anti-Parkinson's disease drug, N-propargyl-1(R)-aminoindan (rasagiline), enhances expression of anti-apoptotic bcl-2 in human dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci Lett. 2002;326:105–108. - PubMed
-
- Bian JS, Yong QC, Pan TT, Feng ZN, Ali MY, Zhou S, et al. Role of hydrogen sulfide in the cardioprotection caused by ischemic preconditioning in the rat heart and cardiac myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;316:670–678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

