The effective fraction isolated from Radix Astragali alleviates glucose intolerance, insulin resistance and hypertriglyceridemia in db/db diabetic mice through its anti-inflammatory activity
- PMID: 20735814
- PMCID: PMC2936435
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-7075-7-67
The effective fraction isolated from Radix Astragali alleviates glucose intolerance, insulin resistance and hypertriglyceridemia in db/db diabetic mice through its anti-inflammatory activity
Abstract
Background: Macrophage infiltration in adipose tissue together with the aberrant production of pro-inflammatory cytokines has been identified as the key link between obesity and its related metabolic disorders. This study aims to isolate bioactive ingredients from the traditional Chinese herb Radix Astragali (Huangqi) that alleviate obesity-induced metabolic damage through inhibiting inflammation.
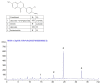
Methods: Active fraction (Rx) that inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine production was identified from Radix Astragali by repeated bioactivity-guided high-throughput screening. Major constituents in Rx were identified by column chromatography followed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass-spectrometry. Anti-diabetic activity of Rx was evaluated in db/db mice.
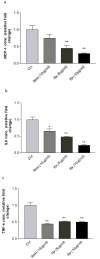
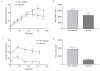
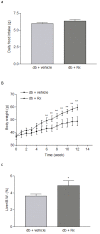
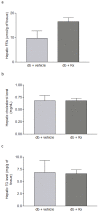
Results: Treatment with Rx, which included calycosin-7-β-D-glucoside (0.9%), ononin (1.2%), calycosin (4.53%) and formononetin (1.1%), significantly reduced the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6 and MCP-1) in human THP-1 macrophages and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced activation of NF-κB in mouse RAW-Blue macrophages in a dose-dependent manner. Chronic administration of Rx in db/db obese mice markedly decreased the levels of both fed and fasting glucose, reduced serum triglyceride, and also alleviated insulin resistance and glucose intolerance when compared to vehicle-treated controls. The mRNA expression levels of inflammatory cell markers CD68 and F4/80, and cytokines MCP-1, TNF-α and IL-6 were significantly reduced in epididymal adipose tissue while the alternatively activated macrophage marker arginase I was markedly increased in the Rx-treated mice.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that suppression of the inflammation pathways in macrophages represents a valid strategy for high-throughput screening of lead compounds with anti-diabetic and insulin sensitizing properties, and further support the etiological role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of obesity-related metabolic disorders.
Figures
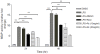



Similar articles
-
Calycosin Ameliorates Diabetes-Induced Renal Inflammation via the NF-κB Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Mar 4;25:1671-1678. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915242. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 30830898 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol alleviates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in db/db mice by inhibiting the STING/NLRP3 signaling pathway.Endocr Connect. 2024 Apr 8;13(5):e230379. doi: 10.1530/EC-23-0379. Print 2024 May 1. Endocr Connect. 2024. PMID: 38466634 Free PMC article.
-
Piperine ameliorates insulin resistance via inhibiting metabolic inflammation in monosodium glutamate-treated obese mice.BMC Endocr Disord. 2020 Oct 7;20(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12902-020-00617-1. BMC Endocr Disord. 2020. PMID: 33028294 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of M1 macrophage activation in adipose tissue by berberine improves insulin resistance.Life Sci. 2016 Dec 1;166:82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.09.025. Epub 2016 Oct 1. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27702567
-
Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006 Mar;17(1):4-12. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006. PMID: 16613757 Review.
Cited by
-
Chinese medicinal formula Fufang Xueshuantong capsule could inhibit the activity of angiotensin converting enzyme.Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014 Mar 4;28(2):322-326. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2014.911611. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014. PMID: 26019516 Free PMC article.
-
A Network Pharmacology Approach to Uncover the Mechanisms of Shen-Qi-Di-Huang Decoction against Diabetic Nephropathy.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Nov 1;2018:7043402. doi: 10.1155/2018/7043402. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30519269 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal Potential of Isoflavonoids: Polyphenols That May Cure Diabetes.Molecules. 2020 Nov 24;25(23):5491. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235491. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33255206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ononin ameliorates inflammation and cartilage degradation in rat chondrocytes with IL-1β-induced osteoarthritis by downregulating the MAPK and NF-κB pathways.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Jan 27;22(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03504-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35086536 Free PMC article.
-
Boiogito, a Kampo medicine, improves hydrarthrosis in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Dec 24;15:451. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0979-7. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26703073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trujillo ME, Scherer PE. Adipose tissue-derived factors: impact on health and disease. Endocr Rev. 2006;27:762–778. - PubMed
-
- Chen HS, Lei J, He X, Wang Y, Wen WW, Wei XZ, Graven-Nielsen T, You HJ, Arendt-Nielsen L. Pivotal involvement of neurogenic mechanism in subcutaneous bee venom-induced inflammation and allodynia in unanesthetized conscious rats. Exp Neurol. 2006;200:386–391. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.02.118. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

