Early CMV viremia is associated with impaired viral control following nonmyeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation with a total lymphoid irradiation and antithymocyte globulin preparative regimen
- PMID: 20736077
- PMCID: PMC5508721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.08.010
Early CMV viremia is associated with impaired viral control following nonmyeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation with a total lymphoid irradiation and antithymocyte globulin preparative regimen
Abstract
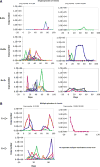
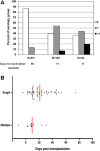
The reconstitution of immune function after hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) plays an important role in the control of viral infections. Both donor and recipient cytomegalovirus (CMV) serostatus has been shown to contribute to effective immune function; however, the influence of a nonmyeloablative preparative (NMA) regimen using total lymphoid irradiation (TLI) and antithymocyte globulin (ATG) on antiviral immune reconstitution has not yet been described. In 117 recipients of NMA HCT patients following ATG and TLI, not unexpectedly, CMV viremia was seen in approximately 60% of the seropositive patients regardless of donor serostatus, and recipient seropositivity significantly increased the odds of CMV viremia after transplant in a multivariate analysis. The administration of ATG and TLI resulted in a strikingly earlier viremia in the posttransplant period when compared to the previously reported timing of viremia following myeloablative preparative regimens, especially for transplant recipients who were seropositive for CMV with seronegative donors. Furthermore, early viremia in the setting of a CMV naïve donor was associated with a delay in functional antiviral control. These observations demonstrate the dynamic nature of immunity in relation to CMV antigen exposure in the complex environment resulting from NMA conditions where both donor and residual recipient immune response affect viral control.
Copyright © 2011 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

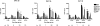

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific T cell immune reconstitution revealed that baseline antiviral immunity, prophylaxis, or preemptive therapy but not antithymocyte globulin treatment contribute to CMV-specific T cell reconstitution in kidney transplant recipients.J Infect Dis. 2010 Aug 15;202(4):585-94. doi: 10.1086/654931. J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20594105
-
Effect of conditioning regimen intensity on CMV infection in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009 Jun;15(6):694-703. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.02.009. Epub 2009 Apr 16. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009. PMID: 19450754 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Donor and Recipient Cytomegalovirus Serostatus on Outcomes of Antithymocyte Globulin-Conditioned Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016 Sep;22(9):1654-1663. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2016.05.020. Epub 2016 May 28. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016. PMID: 27246372
-
Control of Cytomegalovirus Viremia after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Review on CMV-Specific T Cell Reconstitution.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 Sep;24(9):1776-1782. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.03.028. Epub 2018 Apr 4. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018. PMID: 29626514 Review.
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
Cited by
-
Risks and benefits of sex-mismatched hematopoietic cell transplantation differ according to conditioning strategy.Haematologica. 2015 Nov;100(11):1477-85. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2015.125294. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Haematologica. 2015. PMID: 26250581 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cytomegalovirus pneumonia in hematopoietic stem cell recipients.J Intensive Care Med. 2014 Jul-Aug;29(4):200-12. doi: 10.1177/0885066613476454. Epub 2013 Feb 6. J Intensive Care Med. 2014. PMID: 23753231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prophylactic rituximab after allogeneic transplantation decreases B-cell alloimmunity with low chronic GVHD incidence.Blood. 2012 Jun 21;119(25):6145-54. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-395970. Epub 2012 May 4. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22563089 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antithymocyte globulin improves the survival of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome undergoing HLA-matched unrelated donor and haplo-identical donor transplants.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 6;7:43488. doi: 10.1038/srep43488. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28262717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boeckh M, Nichols WG, Papanicolaou G, Rubin R, Wingard JR, Zaia J. Cytomegalovirus in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: current status, known challenges, and future strategies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2003;9:543–558. - PubMed
-
- Lilleri D, Fornara C, Chiesa A, Caldera D, Alessandrino EP, Gerna G. Human cytomegalovirus-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell reconstitution in adult allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients and immune control of viral infection. Haematologica. 2008;93:248–256. - PubMed
-
- Hakki M, Riddell SR, Storek J, et al. Immune reconstitution to cytomegalovirus after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: impact of host factors, drug therapy, and subclinical reactivation. Blood. 2003;102:3060–3067. - PubMed
-
- Cwynarski K, Ainsworth J, Cobbold M, et al. Direct visualization of cytomegalovirus-specific T-cell reconstitution after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2001;97:1232–1240. - PubMed
-
- Lowsky R, Takahashi T, Liu PL, et al. Protective conditioning for acute graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1321–1331. - PubMed

