Genome-wide analysis of thiourea-modulated salinity stress-responsive transcripts in seeds of Brassica juncea: identification of signalling and effector components of stress tolerance
- PMID: 20736293
- PMCID: PMC2958782
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcq163
Genome-wide analysis of thiourea-modulated salinity stress-responsive transcripts in seeds of Brassica juncea: identification of signalling and effector components of stress tolerance
Abstract
Background and aims: Abiotic stresses including salinity are the major constraints to crop production. In this regard, the use of thiourea (TU) in imparting salinity-stress tolerance to Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) has been demonstrated earlier. To gain an insight into the mechanism of TU action, various molecular and biochemical studies were conducted.
Methods: Microarray analysis was performed in seeds subjected to distilled water (control), 1 m NaCl, 1 m NaCl + 6·5 mm TU and 6·5 mm TU alone for 1 h. Real-time PCR validation of selected genes and biochemical studies were conducted under similar treatments at 1 h and 6 h.
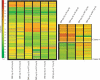
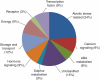
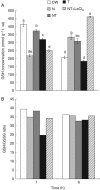
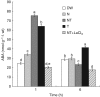
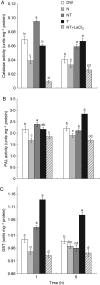
Key results: The microarray analysis revealed a differential expression profile of 33 genes in NaCl- and NaCl + TU-treated seeds, most of which are established markers of stress tolerance. The temporal regulation of eight selected genes by real-time PCR indicated their early and co-ordinated induction at 1 h in NaCl + TU only. Besides, NaCl + TU-treated seeds also maintained a higher level of abscisic acid, reduced to oxidized glutathione (GSH : GSSG) ratio and activities of catalase, phenylalanine ammonia lyase and glutathione-S-transferases, as compared with that of NaCl treatment. The addition of LaCl(3) (a specific calcium-channel blocker) restricted the responses of TU both at molecular and biochemical level suggesting the possible involvement of a cytosolic calcium burst in the TU-mediated response. The TU-alone treatment was comparable to that of the control; however, it reduced the expression of some transcription factors and heat-shock proteins presumably due to the stabilization of the corresponding proteins.
Conclusions: The TU treatment co-ordinately regulates different signalling and effector mechanisms at an early stage to alleviate stress even under a high degree of salinity. This also indicates the potential of TU to be used as an effective bioregulator to impart salinity tolerance under field conditions.
Figures
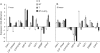
References
-
- Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods in Enzymology. 1984;105:121–26. - PubMed
-
- Anterola AM, Lewis NG. Trends in lignin modification: a comprehensive analysis of the effects of genetic manipulations/mutations on lignifications and vascular integrity. Phytochemistry. 2002;61:221–294. - PubMed
-
- Costa MA, Collins RE, Anterola AM, Cochrane FC, Davin LB, Lewis NG. An in silico assessment of gene function and organization of the phenylpropanoid pathway metabolic networks in Arabidopsis thaliana and limitations thereof. Phytochemistry. 2003;64:1097–1112. - PubMed

