Cyclin-dependent kinase 4-mediated phosphorylation inhibits Smad3 activity in cyclin D-overexpressing breast cancer cells
- PMID: 20736297
- PMCID: PMC3253857
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0537
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4-mediated phosphorylation inhibits Smad3 activity in cyclin D-overexpressing breast cancer cells
Abstract
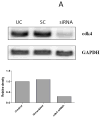
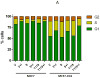
Smad3, a component of the transforming growth factor β signaling cascade, contributes to G(1) arrest in breast cancer cells. Cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) promotes G(1)-S-phase transition, and CDK phosphorylation of Smad3 has been associated with inhibition of Smad3 activity. We hypothesized that overexpression of cyclin D1 exerts tumorigenic effects in breast cancer cells through CDK4-mediated phosphorylation and inhibition of Smad3 and release of G(1) arrest. Real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR and immunoblotting were used to evaluate expression of study proteins in cyclin D1-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Smad3 transcriptional activity and cell cycle control were examined in cells transfected with wild-type (WT) Smad3 or Smad3 with single or multiple CDK phosphorylation site mutations (M) in the presence or absence of the CDK4 inhibitor or cotransfection with cdk4 small interfering RNA (siRNA). Transfection of the Smad3 5M construct resulted in decreased c-myc and higher p15(INK4B) expression. Compared with WT Smad3, overexpression of the Smad3 T8, T178, 4M, or 5M mutant constructs resulted in higher Smad3 transcriptional activity. Compared with cells transfected with WT Smad3, Smad3 transcriptional activity was higher in cells overexpressing Smad3 mutant constructs and treated with the CDK4 inhibitor or transfected with cdk4 siRNA. Cells transfected with Smad3 T8 or T178 and treated with the CDK4 inhibitor showed an increase in the G(1) cell population. Inhibition of CDK-mediated Smad3 phosphorylation released cyclin D1-regulated blockade of Smad3 transcriptional activity and recovered cell cycle arrest in breast cancer cells. Targeted inhibition of CDK4 activity may have a role in the treatment of cyclin D-overexpressing breast cancers.
Figures







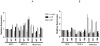







Similar articles
-
CDK4 inhibition and doxorubicin mediate breast cancer cell apoptosis through Smad3 and survivin.Cancer Biol Ther. 2014 Oct;15(10):1301-11. doi: 10.4161/cbt.29693. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25006666 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of cyclin E overexpression on Smad3 activity in breast cancer cell lines.Cell Cycle. 2010 Dec 15;9(24):4900-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.24.14158. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 21150326 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of CDK-mediated phosphorylation of Smad3 results in decreased oncogenesis in triple negative breast cancer cells.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(20):3191-201. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.950126. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25485498 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Smad antiproliferative function by CDK phosphorylation.Cell Cycle. 2005 Jan;4(1):63-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.1.1366. Epub 2005 Jan 12. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 15611645 Review.
-
Targeting CDK4 and CDK6: From Discovery to Therapy.Cancer Discov. 2016 Apr;6(4):353-67. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0894. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Cancer Discov. 2016. PMID: 26658964 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative study of the effects of PEGylated interferon-α2a versus 5-fluorouracil on cancer stem cells in a rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Feb;37(2):1617-25. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3920-2. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26304505
-
Synergistic effect of eribulin and CDK inhibition for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 10;8(48):83925-83939. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20202. eCollection 2017 Oct 13. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29137393 Free PMC article.
-
Cdk4/6 inhibition induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances invasiveness in pancreatic cancer cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Oct;11(10):2138-48. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0562. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22869556 Free PMC article.
-
Effects on human transcriptome of mutated BRCA1 BRCT domain: a microarray study.BMC Cancer. 2012 May 30;12:207. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-207. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22646717 Free PMC article.
-
The Evolving Pathways of the Efficacy of and Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 2;15(19):4835. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194835. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835528 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brown KA, Pietenpol JA, Moses HL. A tale of two proteins: differential roles and regulation of Smad2 and Smad3 in TGF-beta signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2007;101(1):9–33. - PubMed
-
- Yue J, Mulder KM. Transforming growth factor-beta signal transduction in epithelial cells. Pharmacol Ther. 2001;91(1):1–34. - PubMed
-
- Massague J. TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:753–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

