Leiomodin-2 is an antagonist of tropomodulin-1 at the pointed end of the thin filaments in cardiac muscle
- PMID: 20736303
- PMCID: PMC2931607
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.071837
Leiomodin-2 is an antagonist of tropomodulin-1 at the pointed end of the thin filaments in cardiac muscle
Abstract
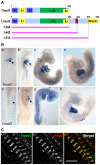
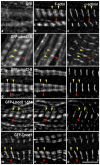
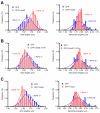
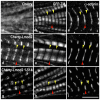
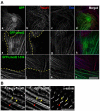
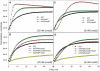
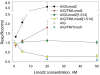
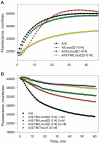
Regulation of actin filament assembly is essential for efficient contractile activity in striated muscle. Leiomodin is an actin-binding protein and homolog of the pointed-end capping protein, tropomodulin. These proteins are structurally similar, sharing a common domain organization that includes two actin-binding sites. Leiomodin also contains a unique C-terminal extension that has a third actin-binding WH2 domain. Recently, the striated-muscle-specific isoform of leiomodin (Lmod2) was reported to be an actin nucleator in cardiomyocytes. Here, we have identified a function of Lmod2 in the regulation of thin filament lengths. We show that Lmod2 localizes to the pointed ends of thin filaments, where it competes for binding with tropomodulin-1 (Tmod1). Overexpression of Lmod2 results in loss of Tmod1 assembly and elongation of the thin filaments from their pointed ends. The Lmod2 WH2 domain is required for lengthening because its removal results in a molecule that caps the pointed ends similarly to Tmod1. Furthermore, Lmod2 transcripts are first detected in the heart after it has begun to beat, suggesting that the primary function of Lmod2 is to maintain thin filament lengths in the mature heart. Thus, Lmod2 antagonizes the function of Tmod1, and together, these molecules might fine-tune thin filament lengths.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leiomodin creates a leaky cap at the pointed end of actin-thin filaments.PLoS Biol. 2020 Sep 8;18(9):e3000848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000848. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Biol. 2020. Update in: PLoS Biol. 2025 Jan 30;23(1):e3003027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003027. PMID: 32898131 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Localization of the binding interface between leiomodin-2 and α-tropomyosin.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1864(5):523-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.02.009. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26873245 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of thin filament assembly in embryonic chick cardiac myocytes: tropomodulin requires tropomyosin for assembly.J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(3):683-95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.3.683. J Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7730404 Free PMC article.
-
Capping actin filament growth: tropomodulin in muscle and nonmuscle cells.Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1997;52:79-89. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1997. PMID: 9210222 Review.
-
Tropomodulin capping of actin filaments in striated muscle development and physiology.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:103069. doi: 10.1155/2011/103069. Epub 2011 Oct 17. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 22013379 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo elongation of thin filaments results in heart failure.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 3;15(1):e0226138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226138. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31899774 Free PMC article.
-
DAAM is required for thin filament formation and Sarcomerogenesis during muscle development in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2014 Feb 27;10(2):e1004166. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004166. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24586196 Free PMC article.
-
A two-segment model for thin filament architecture in skeletal muscle.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;14(2):113-9. doi: 10.1038/nrm3510. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23299957 Free PMC article.
-
Z-line formins promote contractile lattice growth and maintenance in striated muscles of C. elegans.J Cell Biol. 2012 Jul 9;198(1):87-102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201202053. Epub 2012 Jul 2. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22753896 Free PMC article.
-
Functional regulatory mechanism of smooth muscle cell-restricted LMOD1 coronary artery disease locus.PLoS Genet. 2018 Nov 16;14(11):e1007755. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007755. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30444878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almenar-Queralt A., Lee A., Conley C. A., Ribas de Pouplana L., Fowler V. M. (1999). Identification of a novel tropomodulin isoform, skeletal tropomodulin, that caps actin filament pointed ends in fast skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 28466-28475 - PubMed
-
- Babcock G. G., Fowler V. M. (1994). Isoform-specific interaction of tropomodulin with skeletal muscle and erythrocyte tropomyosins. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 27510-27518 - PubMed
-
- Bai J., Hartwig J. H., Perrimon N. (2007). SALS, a WH2-domain-containing protein, promotes sarcomeric actin filament elongation from pointed ends during Drosophila muscle growth. Dev. Cell 13, 828-842 - PubMed
-
- Baker R. K., Antin P. B. (2003). Ephs and ephrins during early stages of chick embryogenesis. Dev. Dyn. 228, 128-142 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein B. W., Bamburg J. R. (1982). Tropomyosin binding to F-actin protects the F-actin from disassembly by brain actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF). Cell Motil. 2, 1-8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

