Activating stress-activated protein kinase-mediated cell death and inhibiting epidermal growth factor receptor signaling: a promising therapeutic strategy for prostate cancer
- PMID: 20736346
- PMCID: PMC2948854
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0180
Activating stress-activated protein kinase-mediated cell death and inhibiting epidermal growth factor receptor signaling: a promising therapeutic strategy for prostate cancer
Abstract
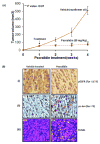
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation is an important event that regulates mitogenic signaling, such as the Raf, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 cascades. EGFR activation has been implicated in the transition of prostate cancer from androgen dependence to independence. Therefore, inhibition of EGFR may effectively suppress prostate cancer growth and progression. The goal of this study was to determine whether the natural compound psoralidin alters EGFR-mediated signaling resulting in the inhibition of prostate cancer growth. Results suggest that inhibition of EGFR alone (by serum deprivation) fails to induce stress-mediated protein kinases (SAPK), namely, Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase/c-Jun signaling, in androgen-independent prostate cancer (AIPC) cells. Treatment with psoralidin, however, inhibited both constitutive and EGF-induced EGFR activation and simultaneously triggered SAPK signaling, resulting in the induction of apoptosis in AIPC cells. In addition, psoralidin downregulated EGFR-regulated MAPK signaling and inhibited cell proliferation in AIPC cells. Oral administration of psoralidin effectively suppressed PC-3 xenograft tumors in nude mice. Compared with control tumors, inhibition of pEGFR expression and an increase in the phosphorylation, activation, and nuclear translocation of c-Jun were observed in psoralidin-treated tumor sections. Our studies suggest that psoralidin may be a potent therapeutic agent that modulates EGFR-mediated key epigenetic events in AIPC.
Figures



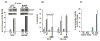
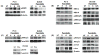
References
-
- Lee TL, Yeh J, Van Waes C, Chen Z. Epigenetic modification of SOCS-1 differentially regulates STAT3 activation in response to interleukin-6 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling through JAK and/or MEK in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5:8–19. - PubMed
-
- Tillotson JK, Rose DP. Endogenous secretion of epidermal growth factor peptides stimulates growth of DU145 prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 1991;60:109–12. - PubMed
-
- Marks RA, Zhang S, Montironi R, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression in prostatic adenocarcinoma after hormonal therapy: a fluorescence in situ hybridization and immunohistochemical analysis. Prostate. 2008;68:919–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

