Matrix metalloproteinase-9 regulates tumor cell invasion through cleavage of protease nexin-1
- PMID: 20736374
- PMCID: PMC3272441
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0242
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 regulates tumor cell invasion through cleavage of protease nexin-1
Abstract
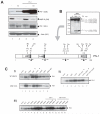
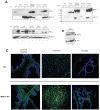
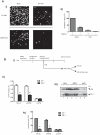
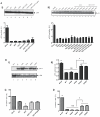
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) expression is known to enhance the invasion and metastasis of tumor cells. In previous work based on a proteomic screen, we identified the serpin protease nexin-1 (PN-1) as a potential target of MMP-9. Here, we show that PN-1 is a substrate for MMP-9 and establish a link between PN-1 degradation by MMP-9 and regulation of invasion. PN-1 levels increased in prostate carcinoma cells after downregulation of MMP-9 and in tissues of MMP-9-deficient mice, consistent with PN-1 degradation by MMP-9. We identified three MMP-9 cleavage sites in PN-1 and showed that mutations in those sites made PN-1 more resistant to MMP-9. Urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) is inhibited by PN-1. MMP-9 augmented uPA activity in the medium of PC3-ML cells by degrading PN-1. Prostate cancer cells, overexpressing PN-1 or treated with MMP-9 shRNA, had reduced cell invasion in Matrigel. PN-1 siRNA restored uPA activity and the invasive capacity. PN-1 mutated in the serpin inhibitory domain, the reactive center loop, failed to inhibit uPA and to reduce Matrigel invasion. This study shows a novel molecular pathway in which MMP-9 regulates uPA activity and tumor cell invasion through cleavage of PN-1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel MMP-9 substrates in cancer cells revealed by a label-free quantitative proteomics approach.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008 Nov;7(11):2215-28. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M800095-MCP200. Epub 2008 Jul 2. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008. PMID: 18596065 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitors regulate cell adhesion through a uPAR-dependent mechanism.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Sep;220(3):655-63. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21806. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19472211 Free PMC article.
-
Protease Nexin-1 affects the migration and invasion of C6 glioma cells through the regulation of urokinase Plasminogen Activator and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9/2.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Nov;1843(11):2631-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.07.008. Epub 2014 Jul 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 25072751
-
[Mechanism of tumor cell-induced extracellular matrix degradation--inhibition of cell-surface proteolytic activity might have a therapeutic effect on tumor cell invasion and metastasis].Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996 Aug;48(8):623-32. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. PMID: 8808830 Review. Japanese.
-
Urokinase/urokinase receptor system: internalization/degradation of urokinase-serpin complexes: mechanism and regulation.Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1995 Mar;376(3):143-55. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1995. PMID: 7612191 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Roles of N-Linked Glycosylation of Human Matrix Metalloproteinase 9.Traffic. 2015 Oct;16(10):1108-26. doi: 10.1111/tra.12312. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Traffic. 2015. PMID: 26207422 Free PMC article.
-
ILT4 facilitates angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Sci. 2024 May;115(5):1459-1475. doi: 10.1111/cas.16126. Epub 2024 Mar 3. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 38433526 Free PMC article.
-
A slow-cycling subpopulation of melanoma cells with highly invasive properties.Oncogene. 2018 Jan 18;37(3):302-312. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.341. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28925403 Free PMC article.
-
Protease nexin 1 induces apoptosis of prostate tumor cells through inhibition of X-chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 28;6(6):3784-96. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2921. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25686839 Free PMC article.
-
The host microenvironment influences prostate cancer invasion, systemic spread, bone colonization, and osteoblastic metastasis.Front Oncol. 2014 Dec 15;4:364. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00364. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25566502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bjorklund M, Koivunen E. Gelatinase-mediated migration and invasion of cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1755:37–69. - PubMed
-
- Coussens LM, Fingleton B, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: trials and tribulations. Science. 2002;295:2387–92. - PubMed
-
- Cauwe B, Van den Steen PE, Opdenakker G. The biochemical, biological, and pathological kaleidoscope of cell surface substrates processed by matrix metalloproteinases. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;42:113–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

