Akt-RSK-S6 kinase signaling networks activated by oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases
- PMID: 20736484
- PMCID: PMC3137639
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2000998
Akt-RSK-S6 kinase signaling networks activated by oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases
Abstract
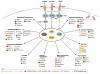
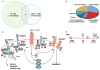
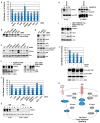
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) activate pathways mediated by serine-threonine kinases, such as the PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase)-Akt pathway, the Ras-MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase)-RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase) pathway, and the mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin)-p70 S6 pathway, that control important aspects of cell growth, proliferation, and survival. The Akt, RSK, and p70 S6 family of protein kinases transmits signals by phosphorylating substrates on an RxRxxS/T motif (R, arginine; S, serine; T, threonine; and x, any amino acid). We developed a large-scale proteomic approach to identify more than 300 substrates of this kinase family in cancer cell lines driven by the c-Met, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), or platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRalpha) RTKs. We identified a subset of proteins with RxRxxS/T sites for which phosphorylation was decreased by RTK inhibitors (RTKIs), as well as by inhibitors of the PI3K, mTOR, and MAPK pathways, and we determined the effects of small interfering RNA directed against these substrates on cell viability. Phosphorylation of the protein chaperone SGTA (small glutamine-rich tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein alpha) at serine-305 was essential for PDGFRalpha stabilization and cell survival in PDGFRalpha-dependent cancer cells. Our approach provides a new view of RTK and Akt-RSK-S6 kinase signaling, revealing previously unidentified Akt-RSK-S6 kinase substrates that merit further consideration as targets for combination therapy with RTKIs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
p90 ribosomal S6 kinase and p70 ribosomal S6 kinase link phosphorylation of the eukaryotic chaperonin containing TCP-1 to growth factor, insulin, and nutrient signaling.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 29;284(22):14939-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900097200. Epub 2009 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19332537 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin-induced growth of pulmonary artery smooth muscle requires activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/serine-threonine protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin/p70 ribosomal S6 kinase 1.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006 Feb;34(2):182-91. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0163OC. Epub 2005 Sep 29. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16195541 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between VEGFR2 and muscarinic receptors regulates the mTOR pathway in serum starved SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells.Cell Signal. 2011 Jan;23(1):239-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.09.008. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 20851763 Free PMC article.
-
Branched-chain amino acids activate key enzymes in protein synthesis after physical exercise.J Nutr. 2006 Jan;136(1 Suppl):269S-73S. doi: 10.1093/jn/136.1.269S. J Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16365096 Review.
-
p70 S6 kinase as a therapeutic target in cancers: More than just an mTOR effector.Cancer Lett. 2022 Jun 1;535:215593. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215593. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35176419 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphoproteomics Meets Chemical Genetics: Approaches for Global Mapping and Deciphering the Phosphoproteome.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 15;21(20):7637. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207637. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33076458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering MET-dependent modulation of global cellular responses to DNA damage by quantitative phosphoproteomics.Mol Oncol. 2020 Jun;14(6):1185-1206. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12696. Epub 2020 May 13. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32336009 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteomic analysis identifies the tumor suppressor PDCD4 as a RSK substrate negatively regulated by 14-3-3.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jul 22;111(29):E2918-27. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1405601111. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25002506 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer systems biology: embracing complexity to develop better anticancer therapeutic strategies.Oncogene. 2015 Jun;34(25):3215-25. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.291. Epub 2014 Sep 15. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25220419 Review.
-
Structural basis for the recognition of kinesin family member 21A (KIF21A) by the ankyrin domains of KANK1 and KANK2 proteins.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 12;293(2):557-566. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.817494. Epub 2017 Nov 28. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29183992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:169–181. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein IB. Cancer. Addiction to oncogenes--the Achilles heal of cancer. Science. 2002;297:63–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

