The contribution of L-arginine to the neurotoxicity of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator following cerebral ischemia: a review of rtPA neurotoxicity
- PMID: 20736961
- PMCID: PMC3023931
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.149
The contribution of L-arginine to the neurotoxicity of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator following cerebral ischemia: a review of rtPA neurotoxicity
Abstract
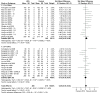
Alteplase is the only drug licensed for acute ischemic stroke, and in this formulation, the thrombolytic agent recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA) is stabilized in a solution of L-arginine. Improved functional outcomes after alteplase administration have been shown in clinical trials, along with improved histological and behavioral measures in experimental models of embolic stroke. However, in animal models of mechanically induced ischemia, alteplase can exacerbate ischemic damage. We have systematically reviewed the literature of both rtPA and L-arginine administration in mechanical focal ischemia. The rtPA worsens ischemic damage under certain conditions, whereas L-arginine can have both beneficial and deleterious effects dependent on the time of administration. The interaction between rtPA and L-arginine may be leading to the production of nitric oxide, which can cause direct neurotoxicity, altered cerebral blood flow, and disruption of the neurovascular unit. We suggest that alternative formulations of rtPA, in the absence of L-arginine, would provide new insight into rtPA neurotoxicity, and have the potential to offer more efficacious thrombolytic therapy for ischemic stroke patients.
Figures




References
-
- Aoki T, Sumii T, Mori T, Wang X, Lo EH. Blood-brain barrier disruption and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression during reperfusion injury: mechanical versus embolic focal ischemia in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke. 2002;33:2711–2717. - PubMed
-
- Armstead WM, Cines DB, Al-Roof Higazi A. Altered NO function contributes to impairment of uPA and tPA cerebrovasodilation after brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21:1204–1211. - PubMed
-
- Armstead WM, Nassar T, Akkawi S, Smith DH, Chen XH, Cines DB, Higazi AA. Neutralizing the neurotoxic effects of exogenous and endogenous tPA. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:1150–1155. - PubMed
-
- Benchenane K, Berezowski V, Ali C, Fernandez-Monreal M, Lopez-Atalaya JP, Brillault J, Chuquet J, Nouvelot A, MacKenzie ET, Bu G, Cecchelli R, Touzani O, Vivien D. Tissue-type plasminogen activator crosses the intact blood-brain barrier by low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-mediated transcytosis. Circulation. 2005;111:2241–2249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

