Final Report of the First Refractory Germ Cell Tumor Treated with Sunitinib Malate
- PMID: 20737043
- PMCID: PMC2914388
- DOI: 10.1159/000260901
Final Report of the First Refractory Germ Cell Tumor Treated with Sunitinib Malate
Abstract
Patients with advanced germ cell tumors can be cured with cisplatin-based chemotherapy, but the outcome remains unsatisfactory for patients with relapsed disease, including those patients with refractory disease after bone marrow transplantation. Targeted therapies have changed the standard of care for many advanced solid tumors. We have identified, in the literature, potential targets for the treatment of refractory germ cell tumors, and applied to a patient with a refractory disease. We chose sunitinib for this purpose. To our knowledge, this is the first case to be treated with sunitinib, and we have found a promising activity.
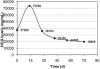
Figures
References
-
- Arora A, Scholar EM. Role of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;315:971–979. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T. Regulation and targets of receptor tyrosine kinases. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38:S3–S10. - PubMed
-
- Mendel DB, Laird AD, Xin X, et al. In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors: determination of a pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:327–337. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–676. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources