Cystoid Macular Edema: Possible Complication of Infliximab Therapy in Behçet's Disease
- PMID: 20737054
- PMCID: PMC2914443
- DOI: 10.1159/000315489
Cystoid Macular Edema: Possible Complication of Infliximab Therapy in Behçet's Disease
Abstract
AIM: Infliximab, an anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha monoclonal antibody, has been reported to be effective in refractory uveoretinitis in Behçet's disease. Because it has been used clinically for a short time, information on its adverse effects is limited. We report a patient who developed cystoid macular edema (CME) following infliximab use for uveoretinitis associated with Behçet's disease. Case Report: A 27-year-old man had refractory uveoretinitis and neuro-Behçet's disease, and intravenous infliximab was administered. RESULTS: One day after infliximab infusion, the patient complained of a decrease in the vision in his left eye. The visual acuity had decreased from 1.2 to 0.5. Daily optical coherence tomographic evaluations showed a progressive worsening of the CME, and fluorescein angiography showed a typical staining with a cystic pattern. Two weeks later, the height of CME appeared to reach a maximum level and thereafter gradually resolved in spite of the continuation of infliximab administration. The visual acuity improved while the patient was treated with repeated subtenon injections of steroids in addition to continuation of infliximab and finally increased from 0.15 to 1.2. CONCLUSIONS: Although the mechanism of CME is not known, clinicians should be aware that infliximab therapy might cause a development and worsening of CME. Thus, it is crucial to rule out preexisting abnormalities in the macula prior to commencing infliximab infusion.
Figures
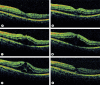
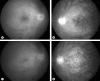
Similar articles
-
The Effect of Infliximab Therapy on Maculopathy in Behcet's Panuveitis: A Case Report.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2011 Sep;2(3):367-75. doi: 10.1159/000335175. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 22220161 Free PMC article.
-
Regression of optic disc neovascularization in patients with Behçet's uveoretinitis after infliximab therapy.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Dec;26(6):627-30. doi: 10.1089/jop.2010.0031. Epub 2010 Nov 2. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 21043804
-
POSSIBLE EFFICACY OF TOPICAL DORZOLAMIDE IN THE TREATMENT OF PACLITAXEL-RELATED CYSTOID MACULAR EDEMA.Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2018 Winter;12(1):75-79. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000433. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2018. PMID: 27749791
-
Frosted branch angiitis and cerebral venous sinus thrombosis as an initial onset of neuro-Behçet's disease: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2017 Apr 15;11(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13256-017-1261-z. J Med Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28410605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behçet's disease; A rare refractory patient with vena cava superior syndrome treated with infliximab: a case report and review of the literature.Acta Clin Belg. 2019 Oct;74(5):364-369. doi: 10.1080/17843286.2018.1522020. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Acta Clin Belg. 2019. PMID: 30220250 Review.
References
-
- Tabbara KF, Al-Hemidan AI. Infliximab effects compared to conventional therapy in the management of retinal vasculitis in Behçet disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008;146:845–850. - PubMed
-
- Yamada Y, Sugita S, Tanaka H, Kamoi K, Kawaguchi T, Mochizuki M. Comparison of infliximab versus cyclosporine during the initial 6-month treatment period in Behçet's disease. Br J Ophthalmol. 2010;94:284–288. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Gonzalez R, Loza E, Jover JA, Benitez Del Castillo JM, Mendez R, Hernandez-Garcia C, Pato E. Treatment of refractory posterior uveitis with infliximab: a 7-year follow-up study. Scand J Rheumatol. 2009;38:58–62. - PubMed
-
- Markomichelakis NN, Theodossiadis PG, Pantelia E, Papaefthimiou S, Theodossiadis GP, Sfikakis PP. Infliximab for chronic cystoid macular edema associated uveitis. Am J Ophtahalmol. 2004;138:648–650. - PubMed
-
- Giganti M, Beer PM, Lemanski N, Hartman C, Schartman J, Falk N. Adverse events after intravitreal infliximab (Remicade) Retina. 2010;30:71–80. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

