Dynamic regulation of sarcomeric actin filaments in striated muscle
- PMID: 20737540
- PMCID: PMC2963174
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.20476
Dynamic regulation of sarcomeric actin filaments in striated muscle
Abstract
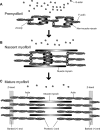
In striated muscle, the actin cytoskeleton is differentiated into myofibrils. Actin and myosin filaments are organized in sarcomeres and specialized for producing contractile forces. Regular arrangement of actin filaments with uniform length and polarity is critical for the contractile function. However, the mechanisms of assembly and maintenance of sarcomeric actin filaments in striated muscle are not completely understood. Live imaging of actin in striated muscle has revealed that actin subunits within sarcomeric actin filaments are dynamically exchanged without altering overall sarcomeric structures. A number of regulators for actin dynamics have been identified, and malfunction of these regulators often result in disorganization of myofibril structures or muscle diseases. Therefore, proper regulation of actin dynamics in striated muscle is critical for assembly and maintenance of functional myofibrils. Recent studies have suggested that both enhancers of actin dynamics and stabilizers of actin filaments are important for sarcomeric actin organization. Further investigation of the regulatory mechanism of actin dynamics in striated muscle should be a key to understanding how myofibrils develop and operate.
© 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Abe H, Obinata T. An actin-depolymerizing protein in embryonic chicken skeletal muscle: purification and characterization. J Biochem. 1989;106:172–180. - PubMed
-
- Abe H, Ohshima S, Obinata T. A cofilin-like protein is involved in the regulation of actin assembly in developing skeletal muscle. J Biochem. 1989;106:696–702. - PubMed
-
- Abe H, Nagaoka R, Obinata T. Cytoplasmic localization and nuclear transport of cofilin in cultured myotubes. Exp Cell Res. 1993;206:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Abe H, Endo T, Yamamoto K, Obinata T. Sequence of cDNAs encoding actin depolymerizing factor and cofilin of embryonic chicken skeletal muscle: two functionally distinct actin-regulatory proteins exhibit high structural homology. Biochemistry. 1990;29:7420–7425. - PubMed
-
- Adams ME, Minamide LS, Duester G, Bamburg JR. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a cDNA encoding chick brain actin depolymerizing factor. Biochemistry. 1990;29:7414–7420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

