Putative tumor suppressor miR-145 inhibits colon cancer cell growth by targeting oncogene Friend leukemia virus integration 1 gene
- PMID: 20737575
- PMCID: PMC2995010
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.25522
Putative tumor suppressor miR-145 inhibits colon cancer cell growth by targeting oncogene Friend leukemia virus integration 1 gene
Abstract
Background: Tumor suppressor microRNA miR-145 is commonly down-regulated in colon carcinoma tissues, but its specific role in tumors remains unknown.
Methods: In this study, the authors identified the Friend leukemia virus integration 1 gene (FLI1) as a novel target of miR-145. FLI1 is involved in t(11;22)(q24:q12) reciprocal chromosomal translocation in Ewing sarcoma, and its expression appears to be associated with biologically more aggressive tumors.
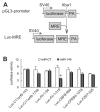
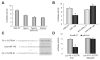
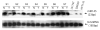
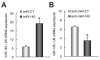
Results: The authors demonstrated that miR-145 targets a putative microRNA regulatory element in the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of FLI1, and its abundance is reversely associated with FLI1 expression in colon cancer tissues and cell lines. By using a luciferase/FLI1 3'-UTR reporter system, they found that miR-145 down-regulated the reporter activity, and this down-regulation was reversed by anti-miR-145. Mutation of the miR-145 microRNA regulatory element sequence in the FLI1 3'-UTR abolished the activity of miR-145. miR-145 decreased FLI1 protein but not FLI1 mRNA, suggesting a mechanism of translational regulation. Furthermore, the authors demonstrated that miR-145 inhibited cell proliferation and sensitized LS174T cells to 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis.
Conclusions: Taken together, these results suggest that miR-145 functions as a tumor suppressor by down-regulating oncogenic FLI1 in colon cancer.
© 2010 American Cancer Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
miR-145 promotes osteosarcoma growth by reducing expression of the transcription factor friend leukemia virus integration 1.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):42241-42251. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9948. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27304058 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an inhibitor of the EWS-FLI1 oncogenic transcription factor by high-throughput screening.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011 Jun 22;103(12):962-78. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr156. Epub 2011 Jun 8. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011. PMID: 21653923 Free PMC article.
-
Hsa-mir-145 is the top EWS-FLI1-repressed microRNA involved in a positive feedback loop in Ewing's sarcoma.Oncogene. 2011 May 5;30(18):2173-80. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.581. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21217773 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting friend leukemia integration 1: A promising approach for prevention and treatment of solid tumors.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;309(Pt 4):143080. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.143080. Epub 2025 Apr 12. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40228766 Review.
-
EWS-FLI1 in Ewing's sarcoma: real targets and collateral damage.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;587:41-52. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-5133-3_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 17163154 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors Affecting EWS-FLI1 Activity in Ewing's Sarcoma.Sarcoma. 2011;2011:352580. doi: 10.1155/2011/352580. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Sarcoma. 2011. PMID: 22135504 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of the Colon Cancer Associated Transcript 2 (CCAT2) Long Non-Coding RNA in Cancer: A Comprehensive Characterization of the Tumorigenic and Molecular Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 19;22(22):12491. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212491. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the relationship between FLI1 and immune infiltrate level in tumour immune microenvironment for breast cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 May;24(10):5501-5514. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15205. Epub 2020 Apr 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32249526 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-145: a potent tumour suppressor that regulates multiple cellular pathways.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Oct;18(10):1913-26. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12358. Epub 2014 Aug 15. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 25124875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs predict and modulate responses to chemotherapy in colorectal cancer.Cell Prolif. 2015 Oct;48(5):503-10. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12202. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Cell Prolif. 2015. PMID: 26202377 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Petersen CP, Bordeleau ME, Pelletier J, Sharp PA. Short RNAs repress translation after initiation in mammalian cells. Mol Cell. 2006;21:533–42. - PubMed
-
- Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Parker R. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006;20:515–24. - PubMed
-
- Zamore PD, Haley B. Ribo-gnome: the big world of small RNAs. Science. 2005;309:1519–24. - PubMed
-
- Cannell IG, Kong YW, Bushell M. How do microRNAs regulate gene expression? Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36:1224–31. - PubMed
-
- Barroso-del Jesus A, Lucena-Aguilar G, Menendez P. The miR-302-367 cluster as a potential stemness regulator in ESCs. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:394–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

