Mechanistic study of gold(I)-catalyzed intermolecular hydroamination of allenes
- PMID: 20738092
- PMCID: PMC2939907
- DOI: 10.1021/ja105530q
Mechanistic study of gold(I)-catalyzed intermolecular hydroamination of allenes
Abstract
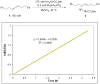
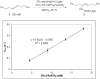
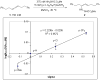
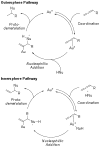
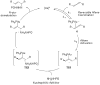
The intermolecular hydroamination of allenes occurs readily with hydrazide nucleophiles, in the presence of 3-12% Ph(3)PAuNTf(2). Mechanistic studies have been conducted to establish the resting state of the gold catalyst, the kinetic order of the reaction, the effect of ligand electronics on the overall rate, and the reversibility of the last steps in the catalytic cycle. We have found the overall reaction to be first order in gold and allene and zero order in nucleophile. Our studies suggest that the rate-limiting transition state for the reaction does not involve the nucleophile and that the active catalyst is monomeric in gold(I). Computational studies support an "outersphere" mechanism and predict that a two-step, no intermediate mechanism may be operative. In accord with this mechanistic proposal, the reaction can be accelerated with the use of more electron-deficient phosphine ligands on the gold(I) catalyst.
Figures




References
-
-
For general reviews, see: Gorin DJ, Sherry BD, Toste FD. Chem Rev. 2008;108:3351.Jiménez-Núñez E, Echavarren AM. Chem Commun. 2007:333.Furstner A, Davies PW. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2007;46:3410.Hashmi ASK. Chem Rev. 2007;107:3180.Shen HC. Tetrahedron. 2008;64:3885.Li Z, Brouwer C, He C. Chem Rev. 2008;108:3239.
-
-
-
For examples, see: Zhang Z, Liu Cong, Kinder RE, Han X, Qian H, Widenhoefer RA. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:9066.Nishina N, Yamamoto Y. Tetrahedron. 2009;65:1799.Duncan AN, Widenhoefer RA. Synlett. 2010:419.Weber D, Tarselli MA, Gagné MR. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;48:5733.
-
-
-
For selected examples, see: Hyland CT, Hegedus LS. J Org Chem. 2006;71:8658.Zhang Z, Bender CF, Widenhoefer RA. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:14148.Liu C, Widenhoefer RA. Org Lett. 2007;9:1935.Piera J, Krumlinde P, Strübing D, Bäckvall JE. Org Lett. 2007;9:2235.Hamilton GL, Kang EJ, Mba M, Toste FD. Science. 2007;317:496.For an example of a gold(I) trimer precatalyst, see: Sherry BD, Maus L, Laforteza BN, Toste FD. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:8132.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

